Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 13 abril 2025

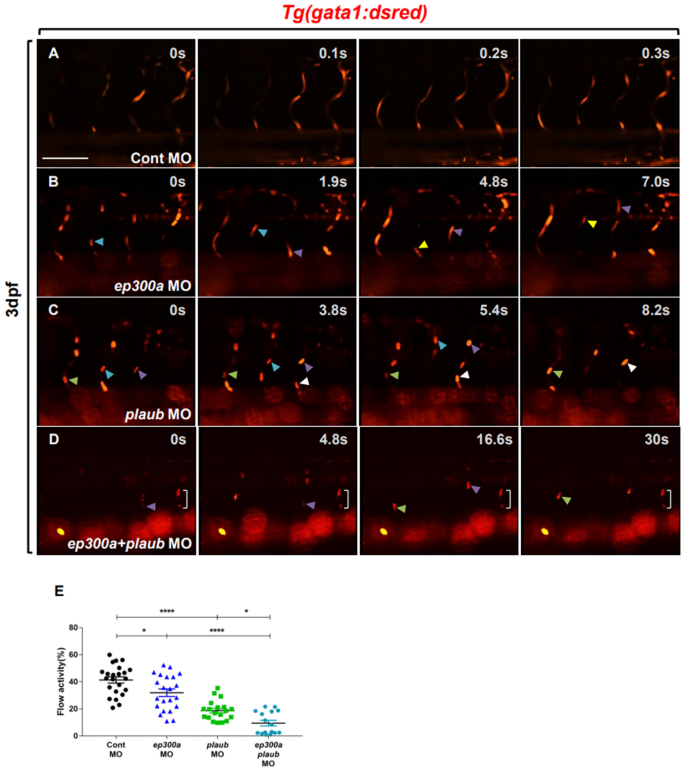
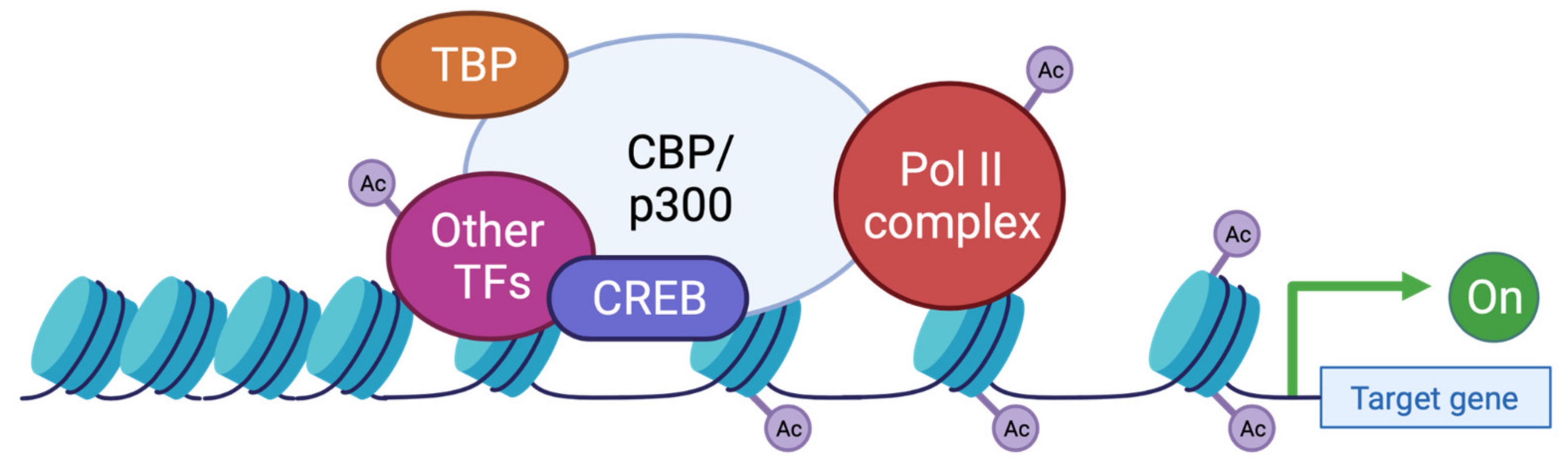
The EP300/CBP inhibitor, C646 affects normal development of zebrafish
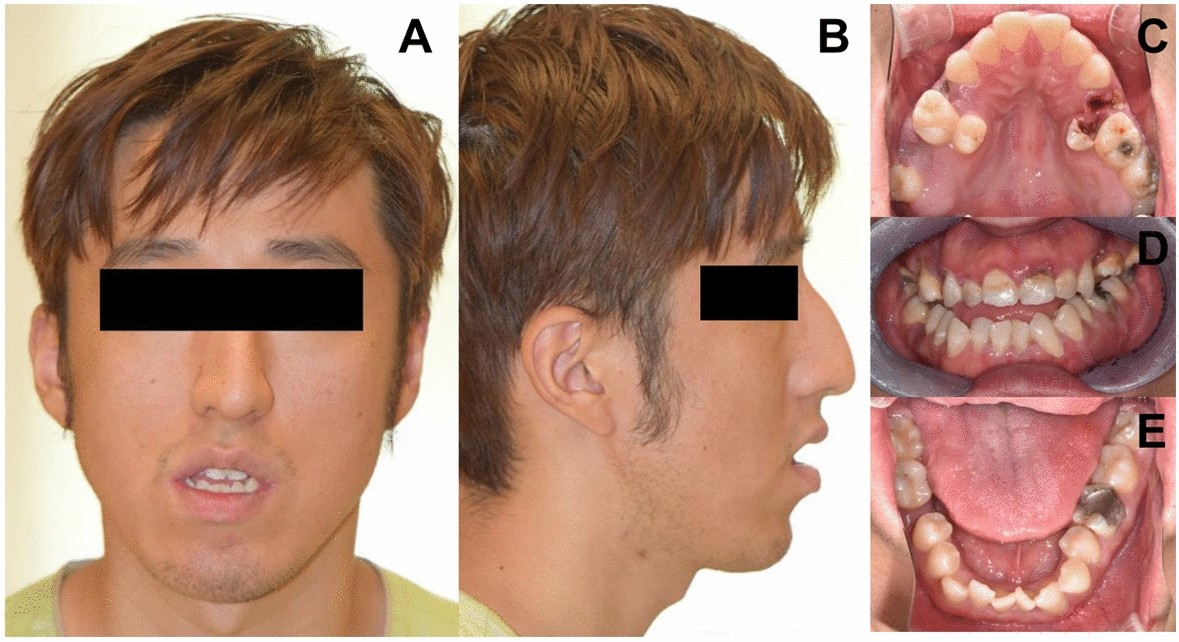
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly

Nail–Patella Syndrome: clinical and molecular data in 55 families raising the hypothesis of a genetic heterogeneity

Genetic Disorder: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews
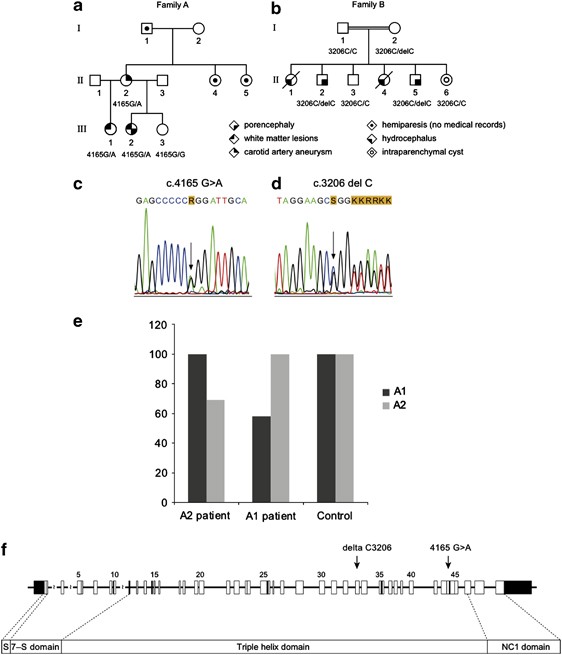
COL4A2 mutation associated with familial porencephaly and small-vessel disease
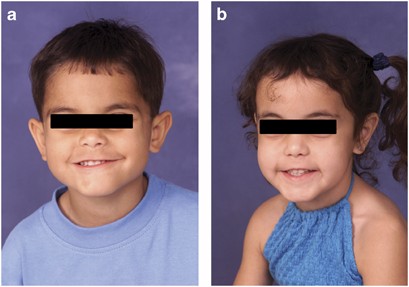
Mutations in COL27A1 cause Steel syndrome and suggest a founder mutation effect in the Puerto Rican population

Otopalatodigital Syndrome, Type Ii disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials

Nuclear Localization signals (NLSs) predicted by PSORTII [21] analysis.

Nervous system defects in the ep300 morphant zebrafish reveals new
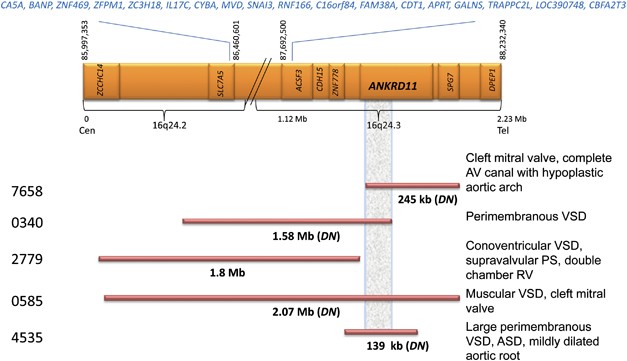
Rare DNA copy number variants in cardiovascular malformations with extracardiac abnormalities

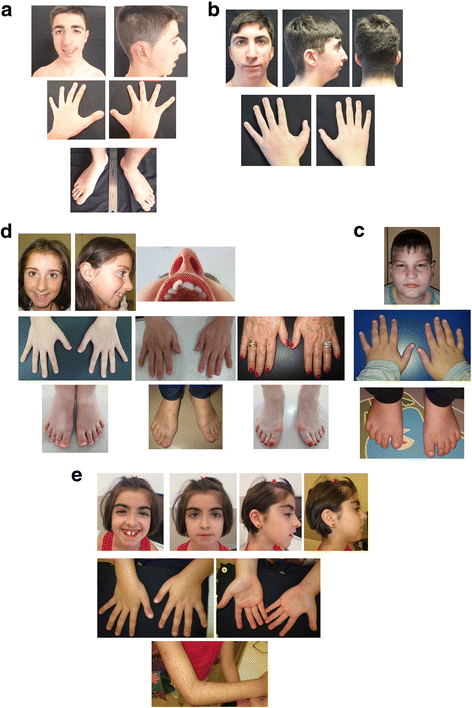
Zebrafish ep300 knockdown models Rubinstein Taybi Syndrome-2. (a-d)
Rubinstein-Taybi 2 associated to novel EP300 mutations: deepening the clinical and genetic spectrum, BMC Medical Genetics
Recomendado para você
-
 Genes, Free Full-Text13 abril 2025
Genes, Free Full-Text13 abril 2025 -
 What Is Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome? - StoryMD13 abril 2025
What Is Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome? - StoryMD13 abril 2025 -
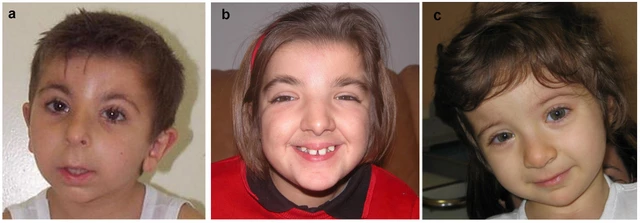
 Facial features of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome13 abril 2025
Facial features of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome13 abril 2025 -
 Silas : Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome » SWEET NECTAR SOCIETY13 abril 2025
Silas : Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome » SWEET NECTAR SOCIETY13 abril 2025 -
DBMCI MDS : Formerly MDS Experts - RUBINSTEIN TAYBI SYNDROME An13 abril 2025
-
Rubinstein Taybi California13 abril 2025
-
Día del Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi – ASOCIACION MEXICANA DE PEDIATRIA13 abril 2025
-
 Silvana é a mãe super-heroína de Lara • História do Dia13 abril 2025
Silvana é a mãe super-heroína de Lara • História do Dia13 abril 2025 -
 O que é síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi? - Crianças Especiais13 abril 2025
O que é síndrome de Rubinstein-Taybi? - Crianças Especiais13 abril 2025 -
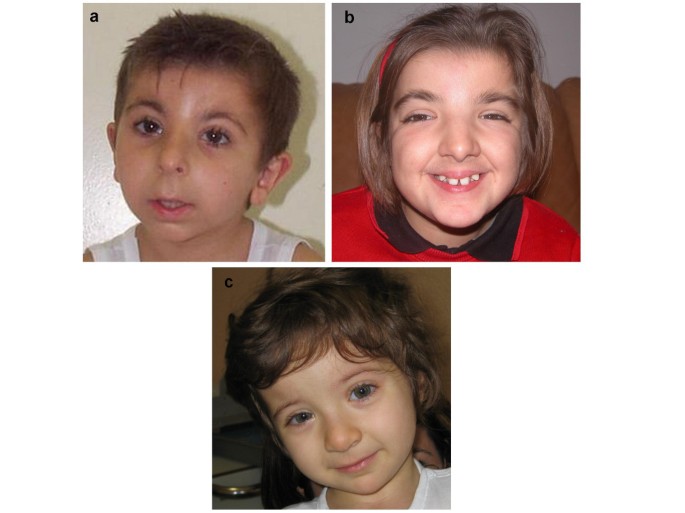 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: spectrum of CREBBP mutations in Italian patients, BMC Medical Genetics13 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: spectrum of CREBBP mutations in Italian patients, BMC Medical Genetics13 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Familia Xerox DC 1213 abril 2025
Familia Xerox DC 1213 abril 2025 -
 Island 02 – Wei Fansub13 abril 2025
Island 02 – Wei Fansub13 abril 2025 -
 Hades Deino, Pokécentral Pixelmon Network Wiki13 abril 2025
Hades Deino, Pokécentral Pixelmon Network Wiki13 abril 2025 -
 Triciclo Infantil Baby Motoca Passeio Velotrol Criança Pedal13 abril 2025
Triciclo Infantil Baby Motoca Passeio Velotrol Criança Pedal13 abril 2025 -
 How to use Xbox Game Pass on LG TVs without a console13 abril 2025
How to use Xbox Game Pass on LG TVs without a console13 abril 2025 -
 Netflix's subscribers surge after password-sharing crackdown, Television13 abril 2025
Netflix's subscribers surge after password-sharing crackdown, Television13 abril 2025 -
 LOL - features of Cyber Sports Competitions13 abril 2025
LOL - features of Cyber Sports Competitions13 abril 2025 -
 DIRT, Grid, and F1 2020 Now Available on EA Play, Xbox Game Pass – GTPlanet13 abril 2025
DIRT, Grid, and F1 2020 Now Available on EA Play, Xbox Game Pass – GTPlanet13 abril 2025 -
 Cash Wizard, Online Slots13 abril 2025
Cash Wizard, Online Slots13 abril 2025 -
 Wallpaper : animals, snow, winter, bears, axes, Vikings TV series, Bj rn Ironside, Alexander Ludwig, weather, 1920x1200 px, vertebrate, dog like mammal, dog breed group 1920x1200 - wallup - 585506 - HD Wallpapers - WallHere13 abril 2025
Wallpaper : animals, snow, winter, bears, axes, Vikings TV series, Bj rn Ironside, Alexander Ludwig, weather, 1920x1200 px, vertebrate, dog like mammal, dog breed group 1920x1200 - wallup - 585506 - HD Wallpapers - WallHere13 abril 2025

