We should avoid the term “fluid overload”, Critical Care
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 março 2025
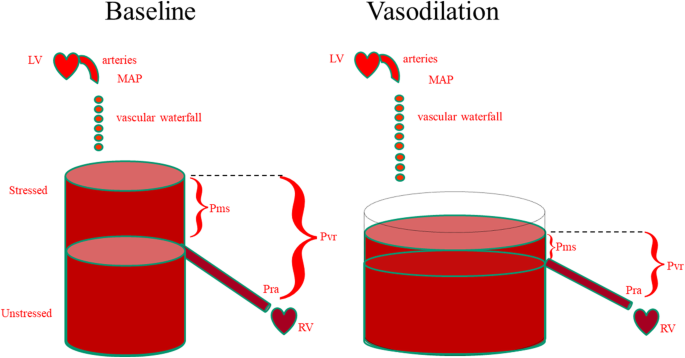

Fluid Overload. Semantic Scholar
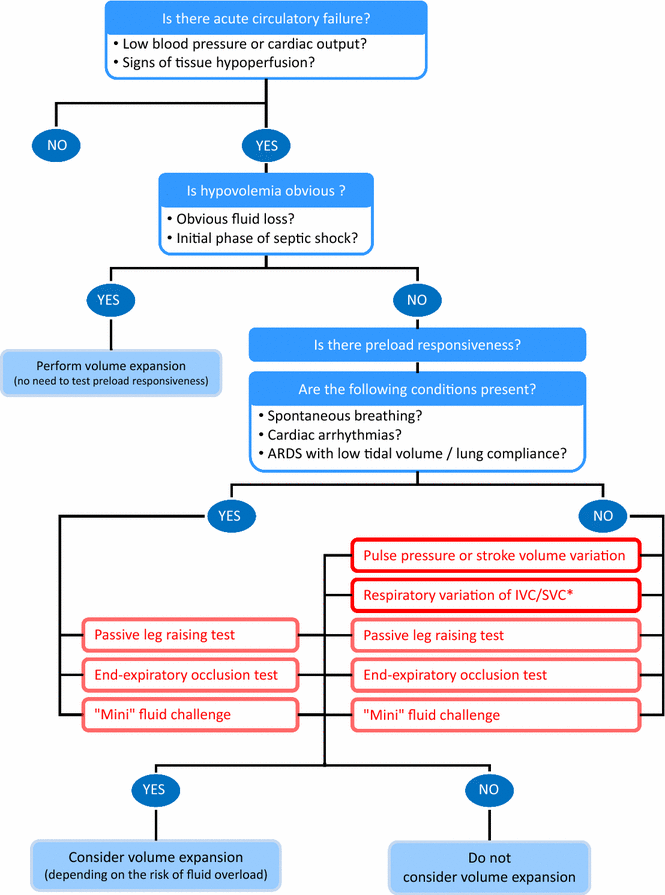
Prediction of fluid responsiveness: an update, Annals of Intensive Care

Fluid Volume Overload and Congestion in Heart Failure
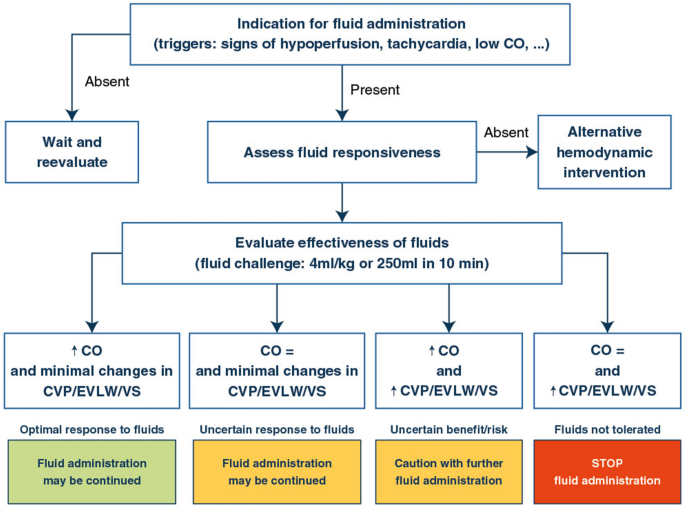
How can assessing hemodynamics help to assess volume status?
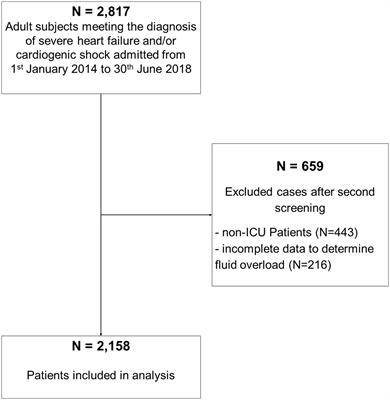
Frontiers Fluid overload and mortality in critically ill patients with severe heart failure and cardiogenic shock–An observational cohort study

Dose–response association between fluid overload and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a multicentre, prospective, observational cohort study
Frontiers Fluid Overload in Critically Ill Children

Fluid Therapy in Veterinary Critical Care

Deresuscitation: Dominating the Diuresis - EMCrit Project
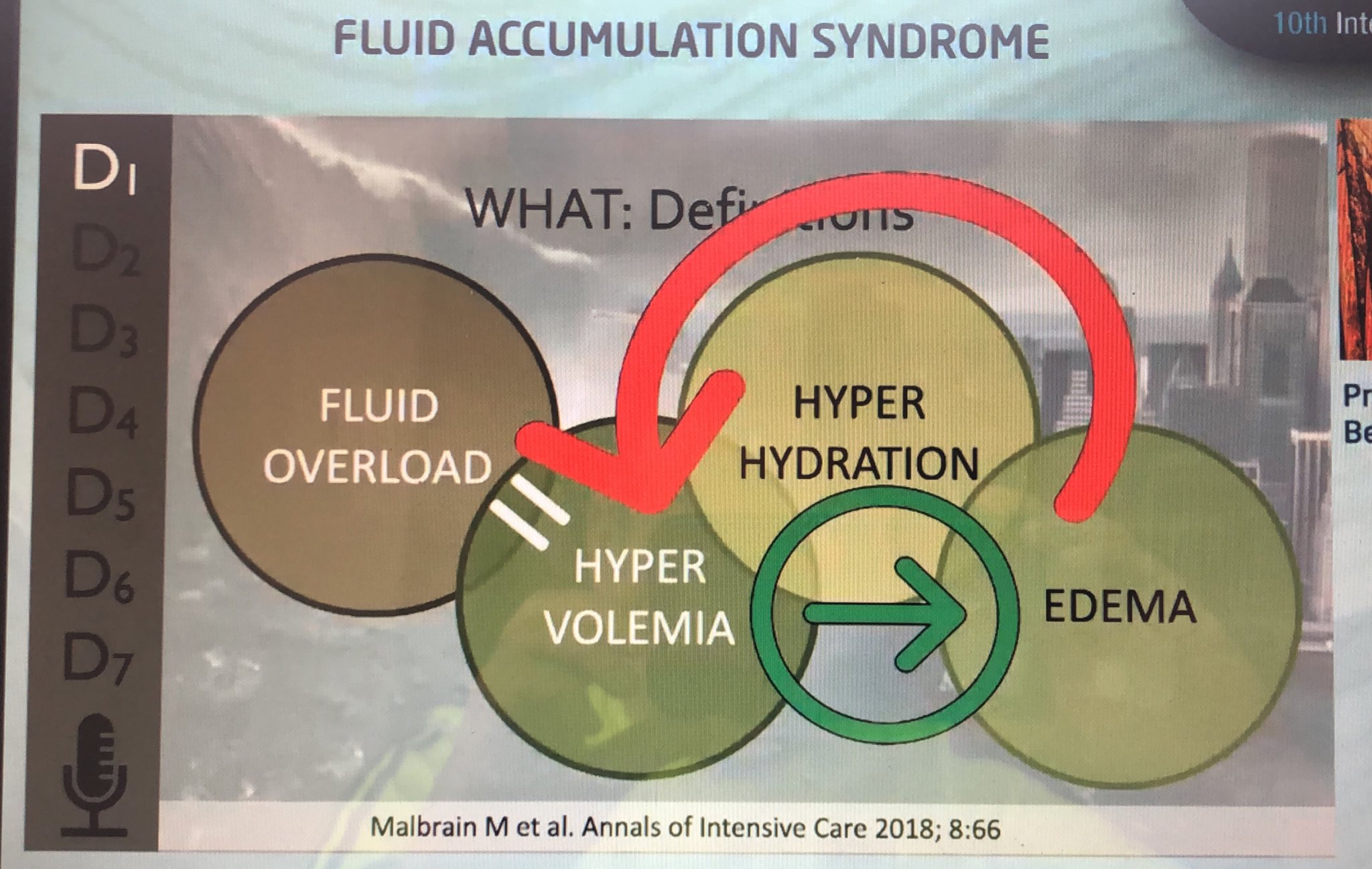
Rolando Claure, MD, FASN, FISN 🇧🇴 on X: Edema does not necessarily = hypervolemia…should we avoid the term fluid overload ? 🤔 #IFAD2021 / X

Fluid balance and outcome in critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (CENTER-TBI and OzENTER-TBI): a prospective, multicentre, comparative effectiveness study - The Lancet Neurology
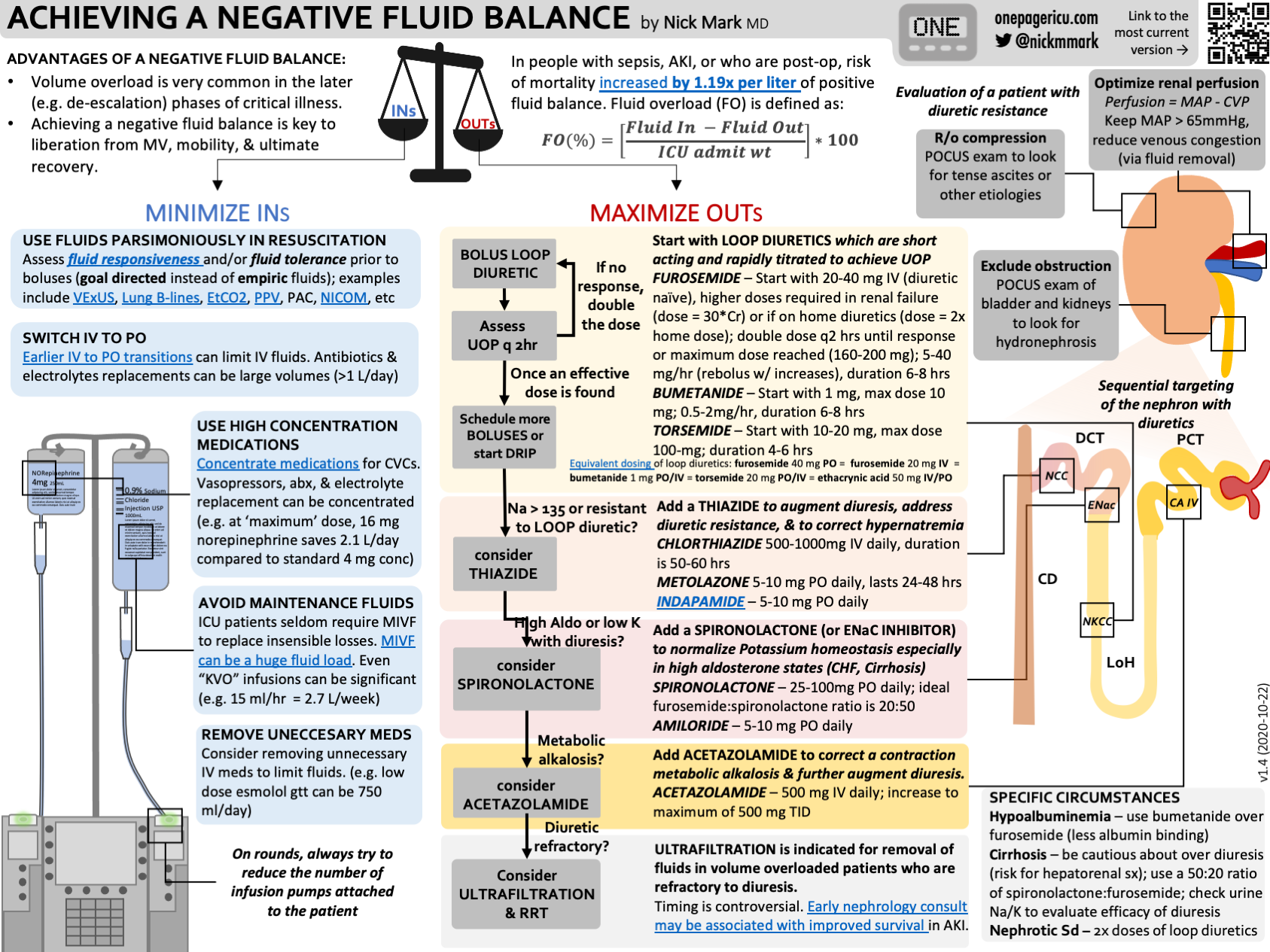
Achieving a Negative Fluid Balance — ICU One Pager

Fluid Therapy in Veterinary Critical Care
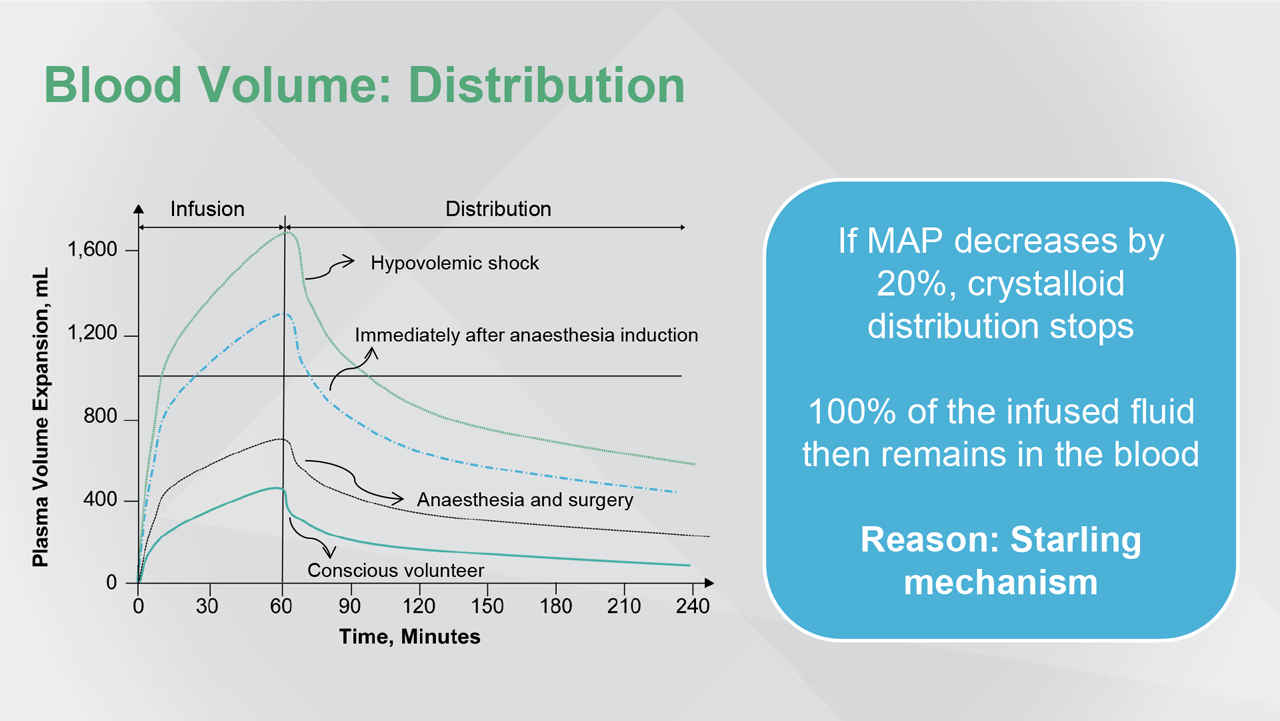
Optimising Fluid Therapy in the Critically Ill - The International Fluid Academy
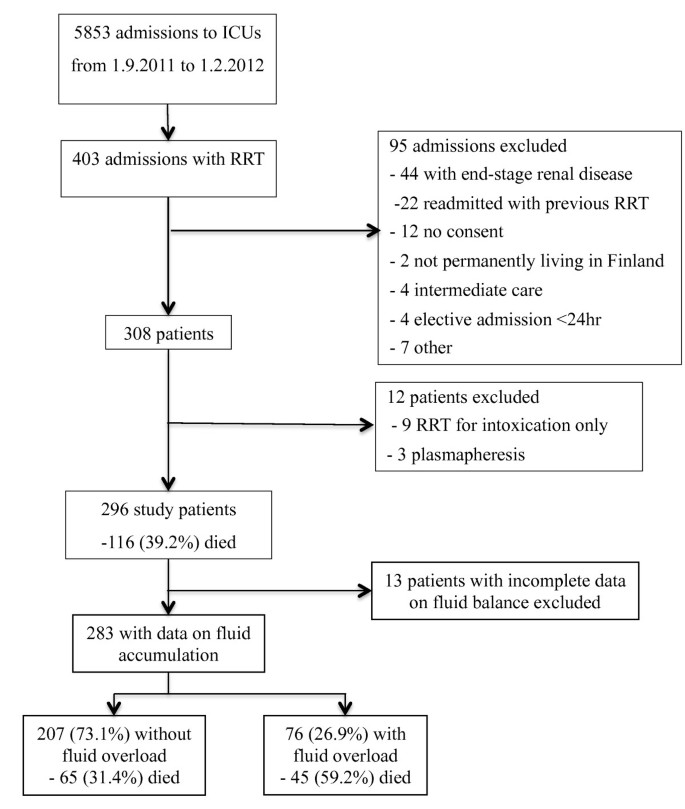
Fluid overload is associated with an increased risk for 90-day mortality in critically ill patients with renal replacement therapy: data from the prospective FINNAKI study, Critical Care
Recomendado para você
-
 Overloading and Overriding in C++28 março 2025
Overloading and Overriding in C++28 março 2025 -
 Information Overload Meaning Business Man Faq Stock Illustration28 março 2025
Information Overload Meaning Business Man Faq Stock Illustration28 março 2025 -
Information Overload in a Post-Twitter, Fake news, Big Data World28 março 2025
-
 Polymorphism in Java - GeeksforGeeks28 março 2025
Polymorphism in Java - GeeksforGeeks28 março 2025 -
 Is Your Circuit Breaker Tripping?28 março 2025
Is Your Circuit Breaker Tripping?28 março 2025 -
 OMG . THE REAL MEANING OF CUTENESS OVERLOAD 😍😍28 março 2025
OMG . THE REAL MEANING OF CUTENESS OVERLOAD 😍😍28 março 2025 -
 C++ Overloading - javatpoint28 março 2025
C++ Overloading - javatpoint28 março 2025 -
 Solved 1. An elevator is designed to tolerate a maximum28 março 2025
Solved 1. An elevator is designed to tolerate a maximum28 março 2025 -
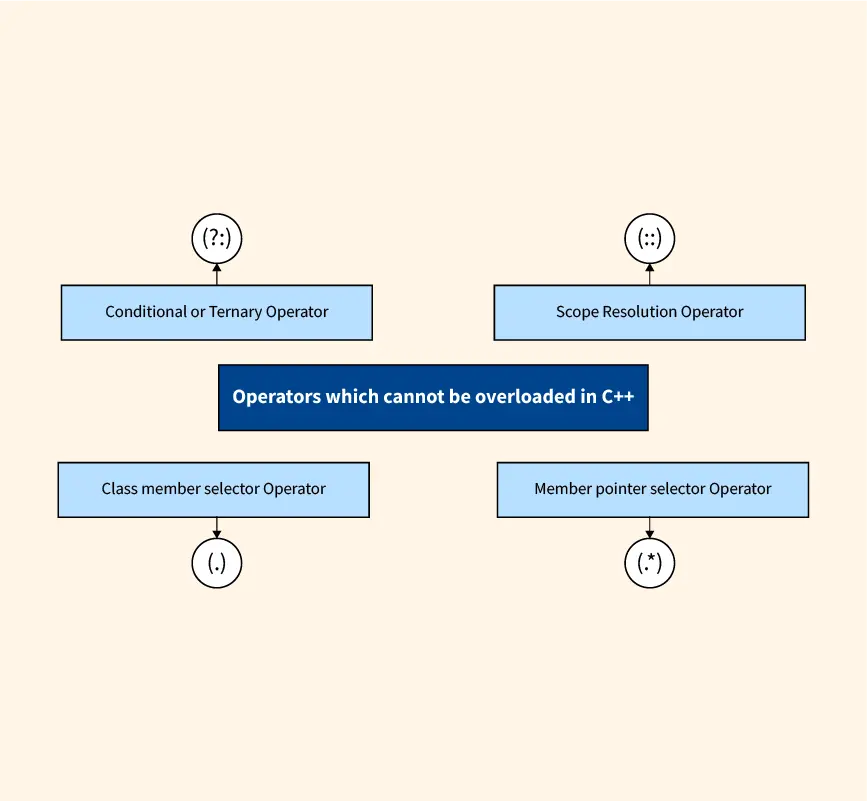 Which Operator Cannot Be Overloaded in C++?28 março 2025
Which Operator Cannot Be Overloaded in C++?28 março 2025 -
 Stressed Word Meaning Stressful Tension And Overload Stock Photo28 março 2025
Stressed Word Meaning Stressful Tension And Overload Stock Photo28 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 AniList Brasil Discord28 março 2025
AniList Brasil Discord28 março 2025 -
 Digimon Adventure 02: The Beginning” ganha trailer nostálgico e28 março 2025
Digimon Adventure 02: The Beginning” ganha trailer nostálgico e28 março 2025 -
 Vídeo mostra PS5 Vs PS4 Pro28 março 2025
Vídeo mostra PS5 Vs PS4 Pro28 março 2025 -
 Top 5 BEST Rake Games (Roblox)28 março 2025
Top 5 BEST Rake Games (Roblox)28 março 2025 -
High Elo Boost San Cristóbal28 março 2025
-
 Baixar Yesterday wo Utatte - Download & Assistir Online! - AnimesTC28 março 2025
Baixar Yesterday wo Utatte - Download & Assistir Online! - AnimesTC28 março 2025 -
 Nova atualização de GTA Online chegando em dezembro - Rockstar Games28 março 2025
Nova atualização de GTA Online chegando em dezembro - Rockstar Games28 março 2025 -
 Pin by Vinn on Widget Rick rolled, Rick astley, Rick28 março 2025
Pin by Vinn on Widget Rick rolled, Rick astley, Rick28 março 2025 -
 DVD Boruto: Naruto Next Generations Episode 1 - 79 English Dubbed EXPEDITE SHIP28 março 2025
DVD Boruto: Naruto Next Generations Episode 1 - 79 English Dubbed EXPEDITE SHIP28 março 2025 -
nr9221922 on X: According to this test, I have 52.8 CPS (Click Per Second). Take this test now to check your CPS score! #CPSTest / X28 março 2025

