Frequency-specific neuromodulation of local and distant
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 março 2025

A growing literature has focused on the brain’s ability to augment processing in local regions by recruiting distant communities of neurons in response to neural decline or insult. In particular, both younger and older adult populations recruit bilateral prefrontal cortex (PFC) as a means of compensating for increasing neural effort to maintain successful cognitive function. However, it remains unclear how local changes in neural activity affect the recruitment of this adaptive mechanism. To address this problem, we combined graph theoretical measures from functional MRI (fMRI) with diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in order to resolve a central hypothesis: how do aged brains flexibly adapt to local changes in cortical activity? Specifically, we applied neuromodulation to increase or decrease local activity in a cortical region supporting successful memory encoding (left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex or DLPFC) using 5Hz or 1Hz rTMS, respectively. We then assessed a region’s local within-module degree (WMD), or the distributed between-module degree (BMD) between distant cortical communities. We predicted that (1) local stimulation-related deficits may be counteracted by boosting BMD between bilateral PFC, and that this effect should be (2) positively correlated with structural connectivity. Both predictions were confirmed; 5Hz rTMS increased local success-related activity and local increases in PFC connectivity, while 1Hz rTMS decreases local activity and triggered a more distributed pattern of bilateral PFC connectivity to compensate for this local inhibitory effect. These results provide an integrated, causal explanation for the network interactions associated with successful memory encoding in older adults.
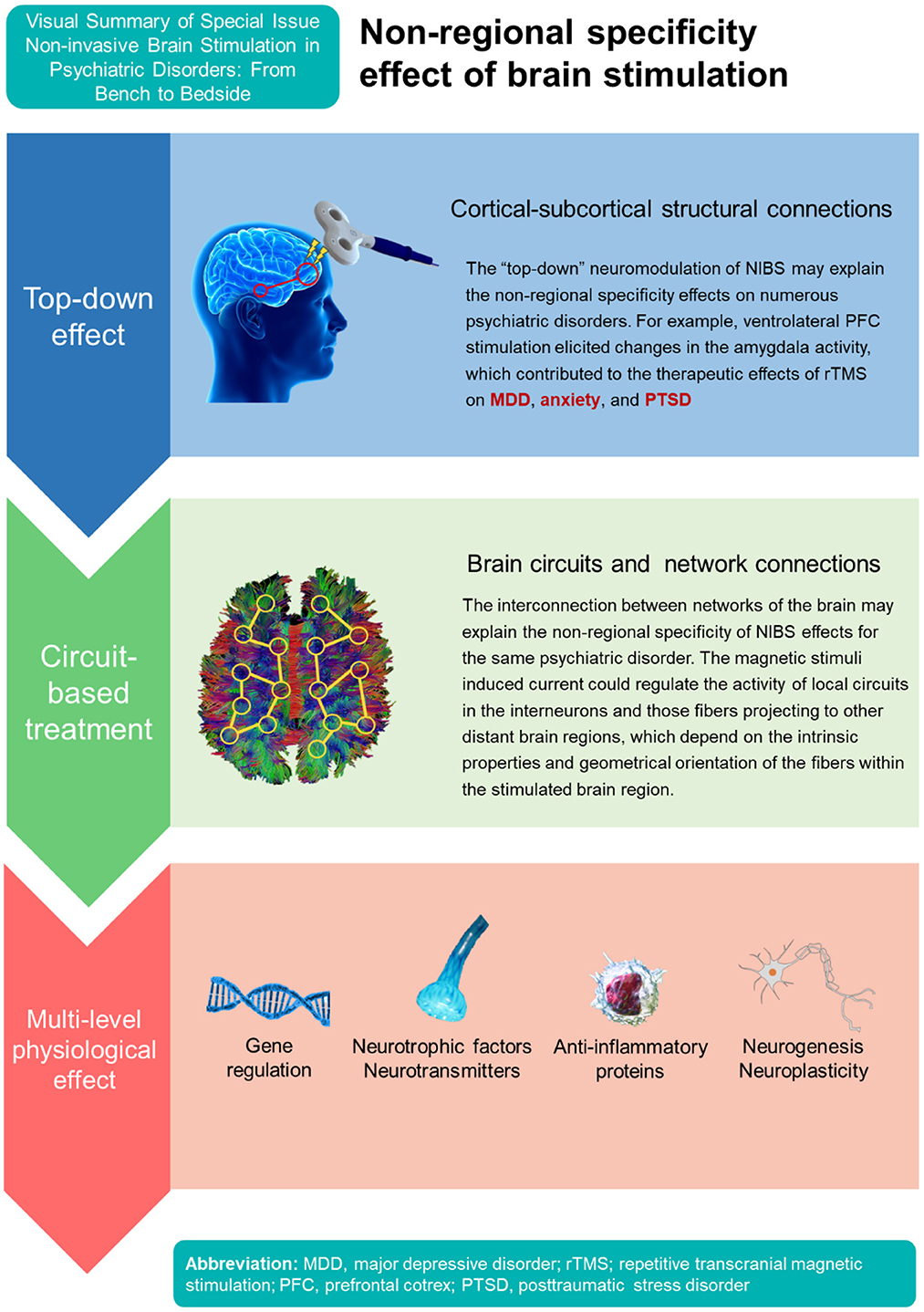
Frontiers Editorial: Non-invasive brain stimulation in

Rhythmic TMS or fluctuating tCS (aka tACS) have been used to

DBS Therapy for Parkinson's Disease

Frequency-specific neuromodulation of local and distant

Integration of reconfigurable microchannels into aligned three
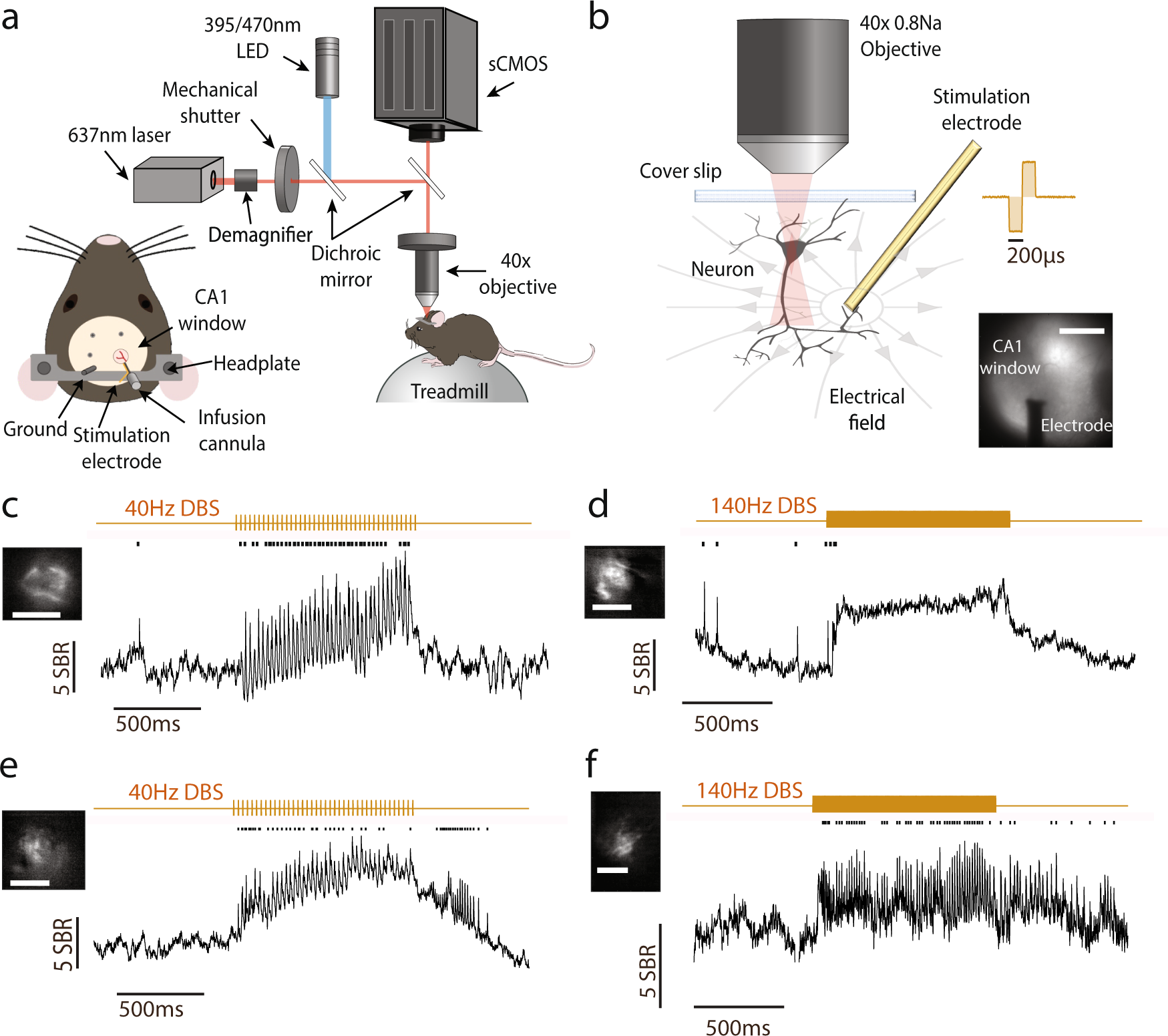
Deep brain stimulation creates informational lesion through

Remote, brain region–specific control of choice behavior with

Frequency-specific neuromodulation of local and distant
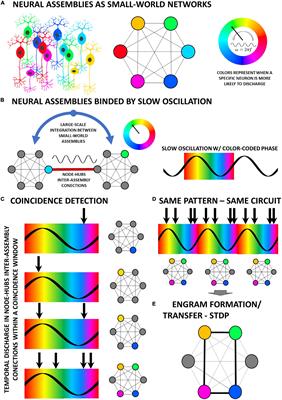
Frontiers On temporal scale-free non-periodic stimulation and
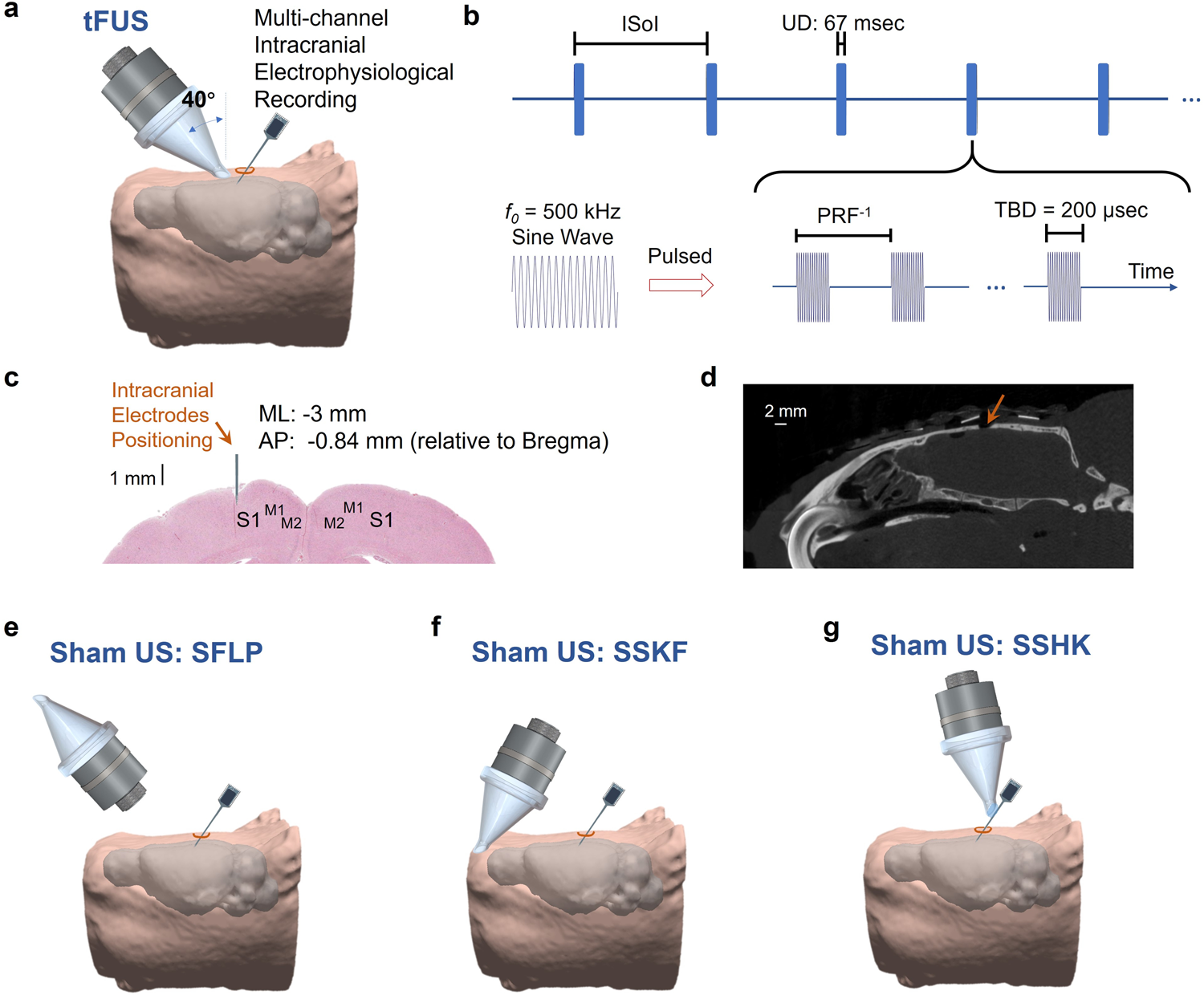
Intrinsic functional neuron-type selectivity of transcranial
Frontiers Non-contact neuromodulation of the human autonomic

Biohybrid nanointerfaces for neuromodulation - ScienceDirect
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
Non-invasive temporal interference electrical stimulation of the

Local and distant cortical responses to single pulse intracranial
Recomendado para você
-
 Brain Test 4 Levels 156, 157, 158, 159, 160 Answers28 março 2025
Brain Test 4 Levels 156, 157, 158, 159, 160 Answers28 março 2025 -
 Brain Test Level 411-415 Walkthrough28 março 2025
Brain Test Level 411-415 Walkthrough28 março 2025 -
 BRAIN TEST NÍVEL 411 EM PORTUGUÊS28 março 2025
BRAIN TEST NÍVEL 411 EM PORTUGUÊS28 março 2025 -
411 #412 #413 #414 #415 #416 #417 #418 #419 #420 #braintest28 março 2025
-
The University of Alabama's Brain-Drone Race Flies Us to a Mind28 março 2025
-
 Expecting 411: Clear Answers & Smart Advice for Your Pregnancy28 março 2025
Expecting 411: Clear Answers & Smart Advice for Your Pregnancy28 março 2025 -
 MicroRNA-411 and Its 5′-IsomiR Have Distinct Targets and Functions28 março 2025
MicroRNA-411 and Its 5′-IsomiR Have Distinct Targets and Functions28 março 2025 -
 Brain Test Level 411 Jawaban - Games For Cats28 março 2025
Brain Test Level 411 Jawaban - Games For Cats28 março 2025 -
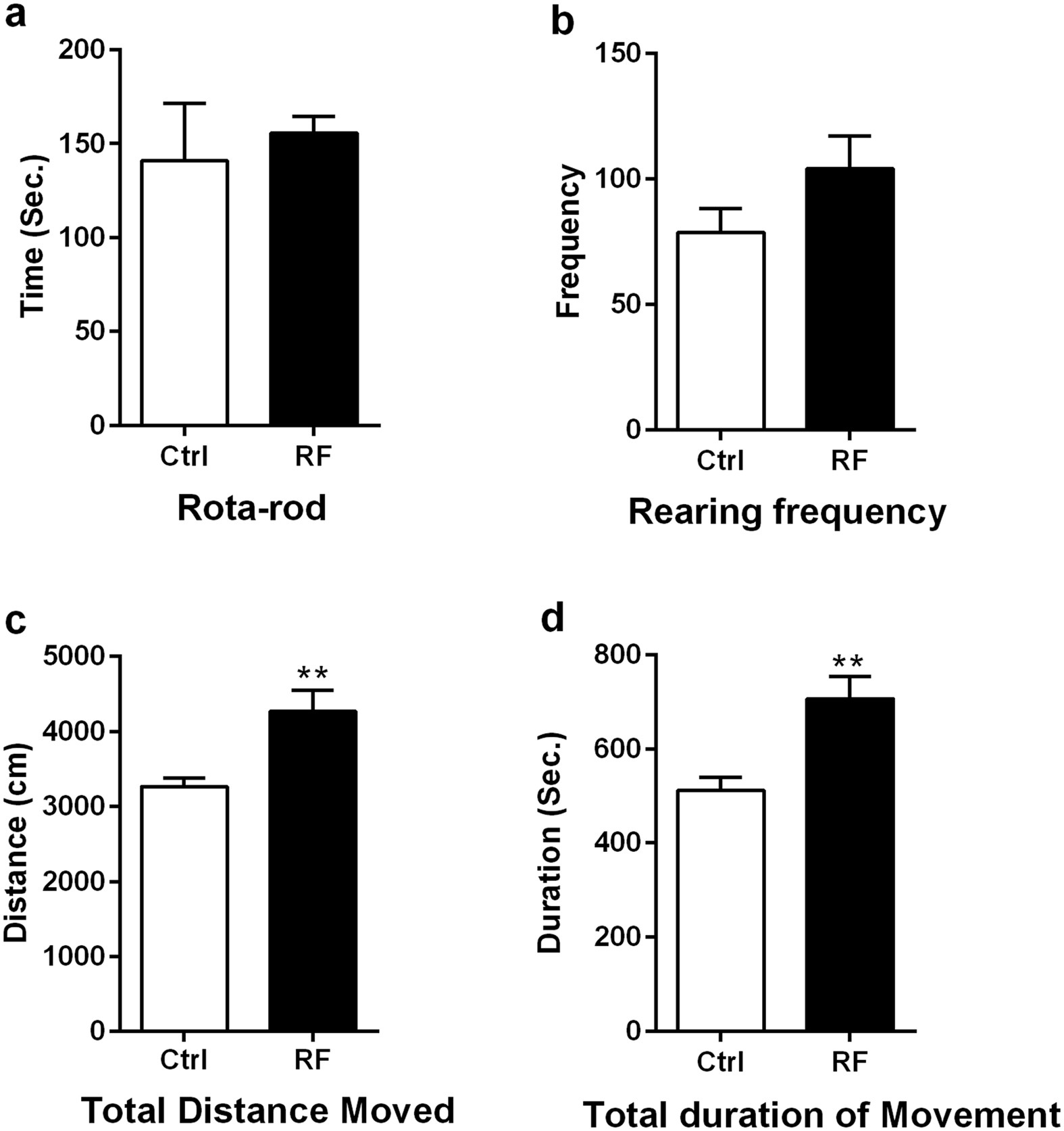 Long-term exposure to 835 MHz RF-EMF induces hyperactivity28 março 2025
Long-term exposure to 835 MHz RF-EMF induces hyperactivity28 março 2025 -
 Liquid Sort Puzzle Water Color Game for Android - Download28 março 2025
Liquid Sort Puzzle Water Color Game for Android - Download28 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Marketing Suite :: Cobrinha BJJ Redondo Beach - Torrance, CA28 março 2025
Marketing Suite :: Cobrinha BJJ Redondo Beach - Torrance, CA28 março 2025 -
 Your Name. Gifs28 março 2025
Your Name. Gifs28 março 2025 -
 Jogo da Memória DPA - Estrela - Estrela28 março 2025
Jogo da Memória DPA - Estrela - Estrela28 março 2025 -
 Palisman, Disney Wiki28 março 2025
Palisman, Disney Wiki28 março 2025 -
 Snake Game – HTML5, JavaScript – Parte 428 março 2025
Snake Game – HTML5, JavaScript – Parte 428 março 2025 -
Force Explorer, PDF, Jedi28 março 2025
-
WeShare - press F for respects28 março 2025
-
 Mah Jongg - Thinking games28 março 2025
Mah Jongg - Thinking games28 março 2025 -
Stamford Bridge has a fresh look!28 março 2025
-
 Shin Ikkitousen – 1 – Zenryoku Fansub28 março 2025
Shin Ikkitousen – 1 – Zenryoku Fansub28 março 2025




