DREAMS: deep read-level error model for sequencing data applied to low-frequency variant calling and circulating tumor DNA detection, Genome Biology
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 março 2025
Circulating tumor DNA detection using next-generation sequencing (NGS) data of plasma DNA is promising for cancer identification and characterization. However, the tumor signal in the blood is often low and difficult to distinguish from errors. We present DREAMS (Deep Read-level Modelling of Sequencing-errors) for estimating error rates of individual read positions. Using DREAMS, we develop statistical methods for variant calling (DREAMS-vc) and cancer detection (DREAMS-cc). For evaluation, we generate deep targeted NGS data of matching tumor and plasma DNA from 85 colorectal cancer patients. The DREAMS approach performs better than state-of-the-art methods for variant calling and cancer detection.

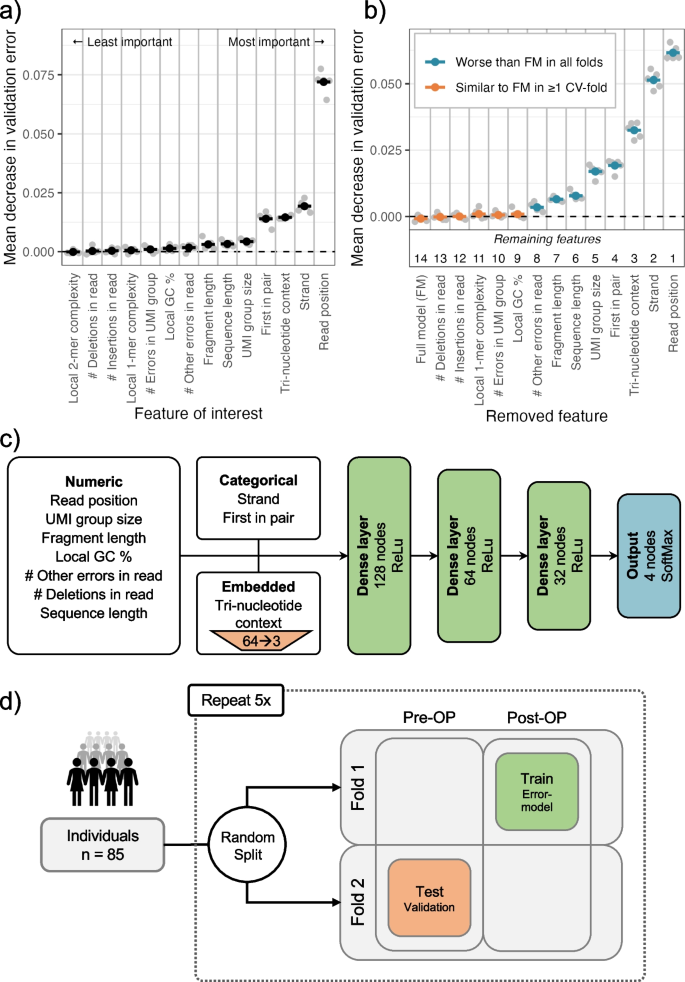
Sequence motifs at systematic error sites. (a) The motif around
Systematic evaluation of error rates and causes in short samples
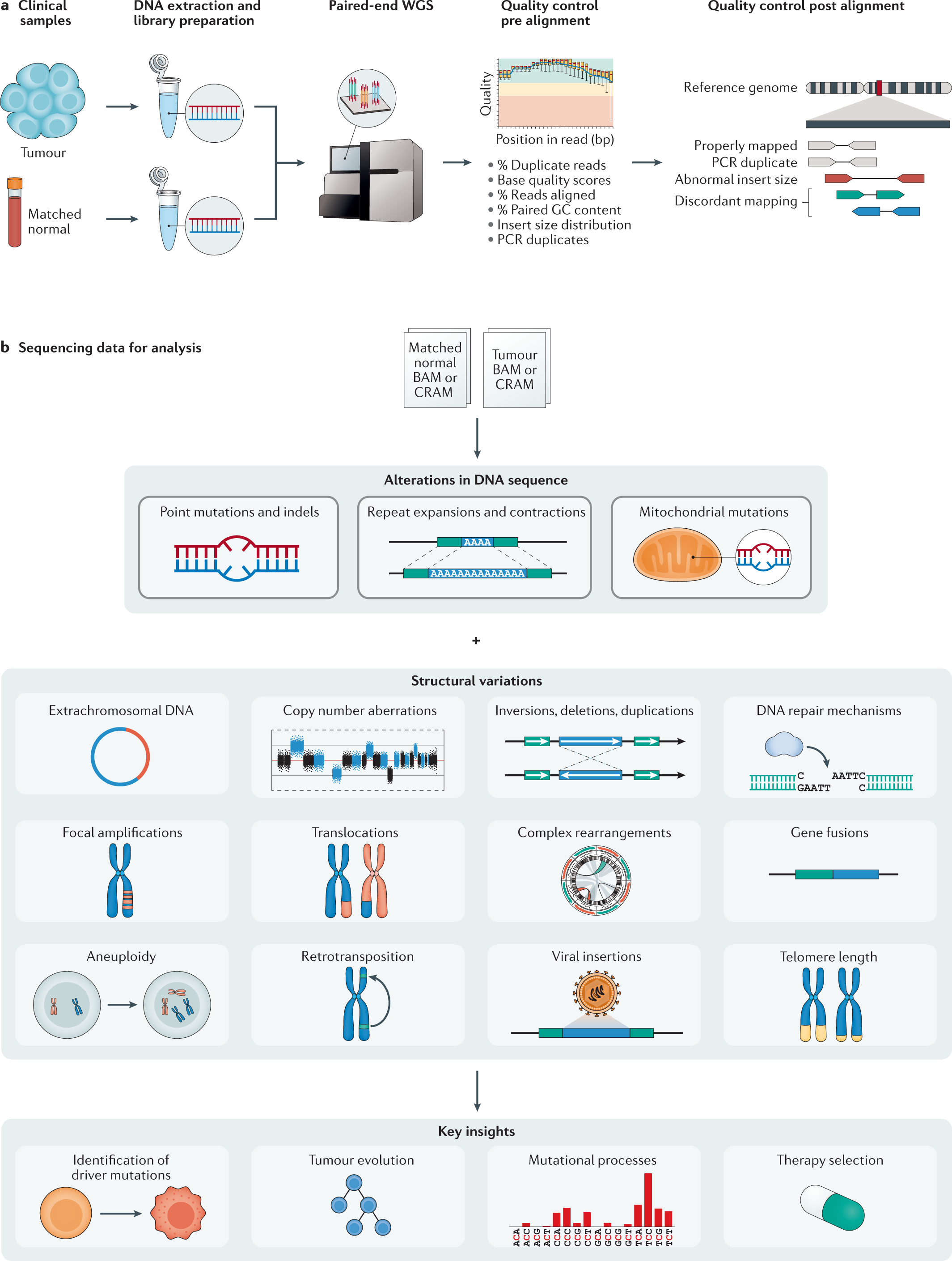
Computational analysis of cancer genome sequencing data
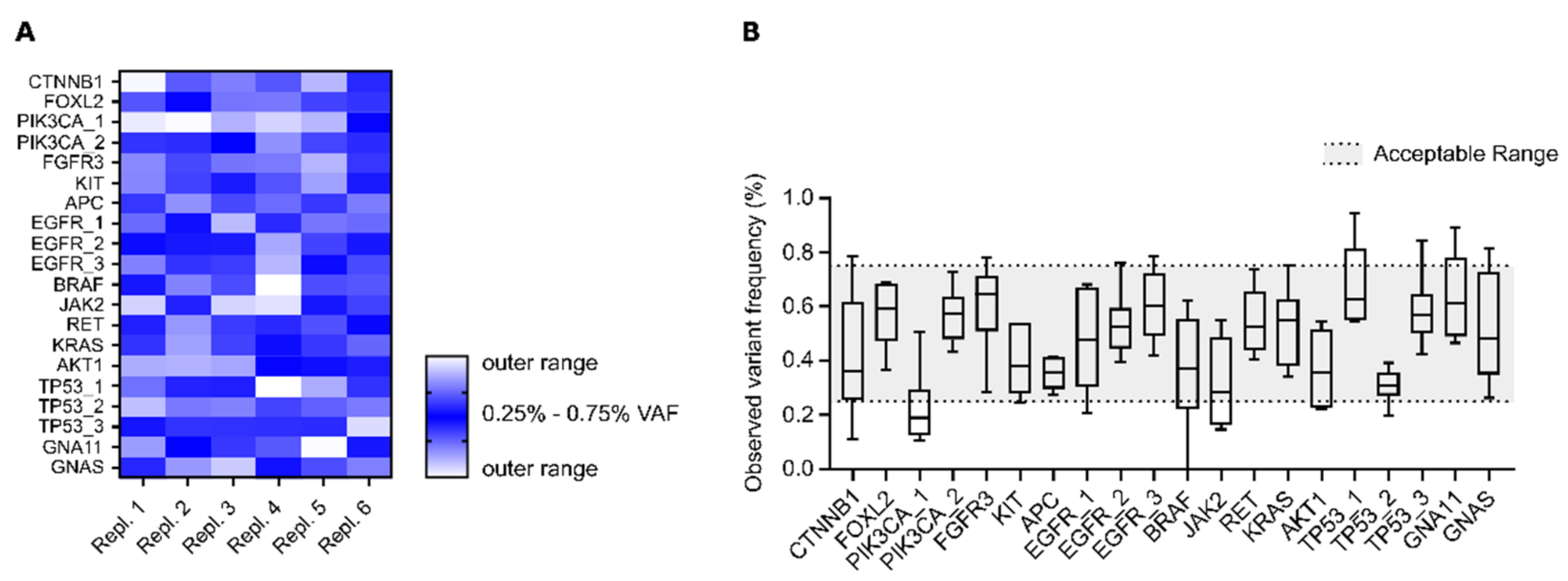
Genes, Free Full-Text
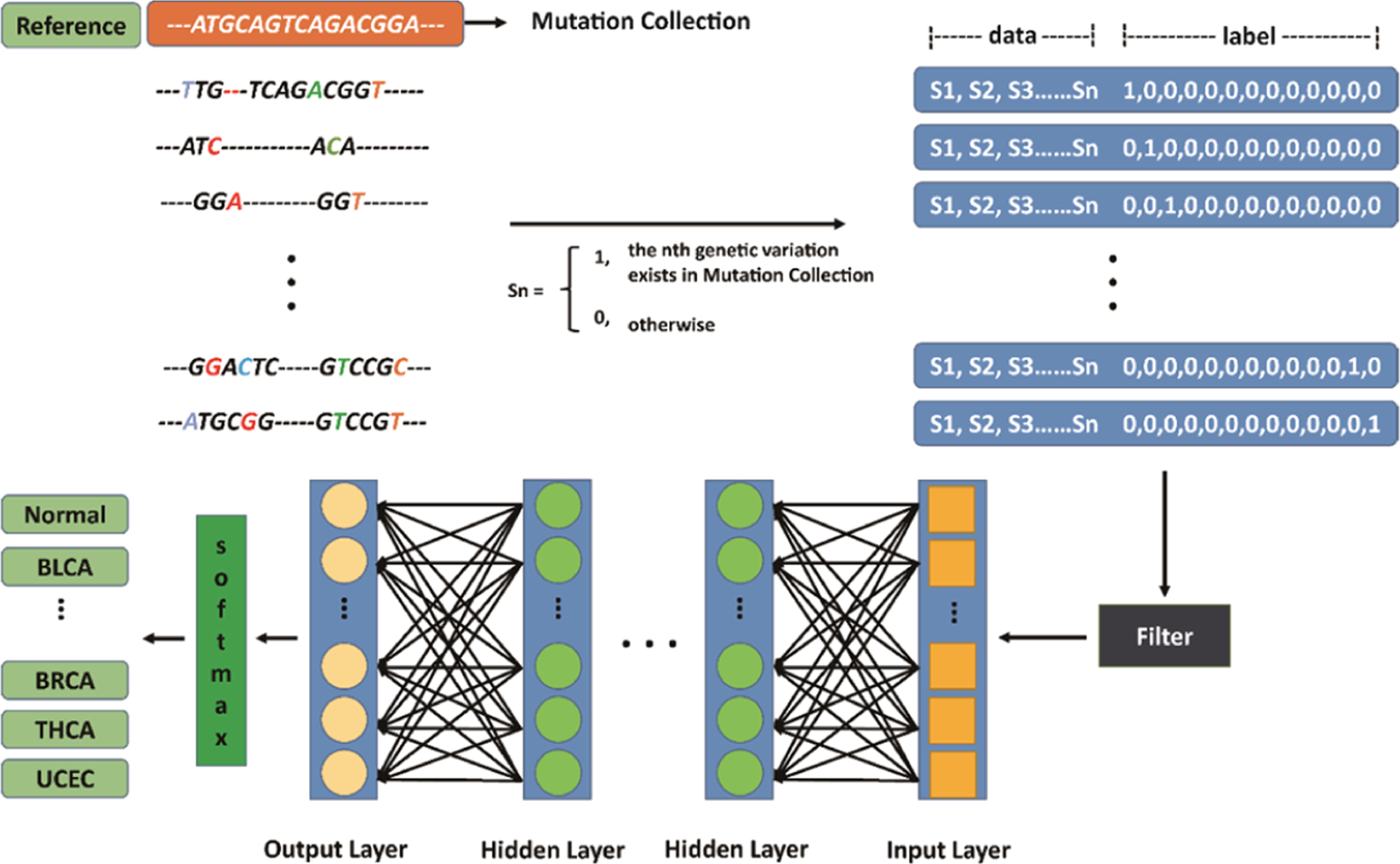
Identification of 12 cancer types through genome deep learning
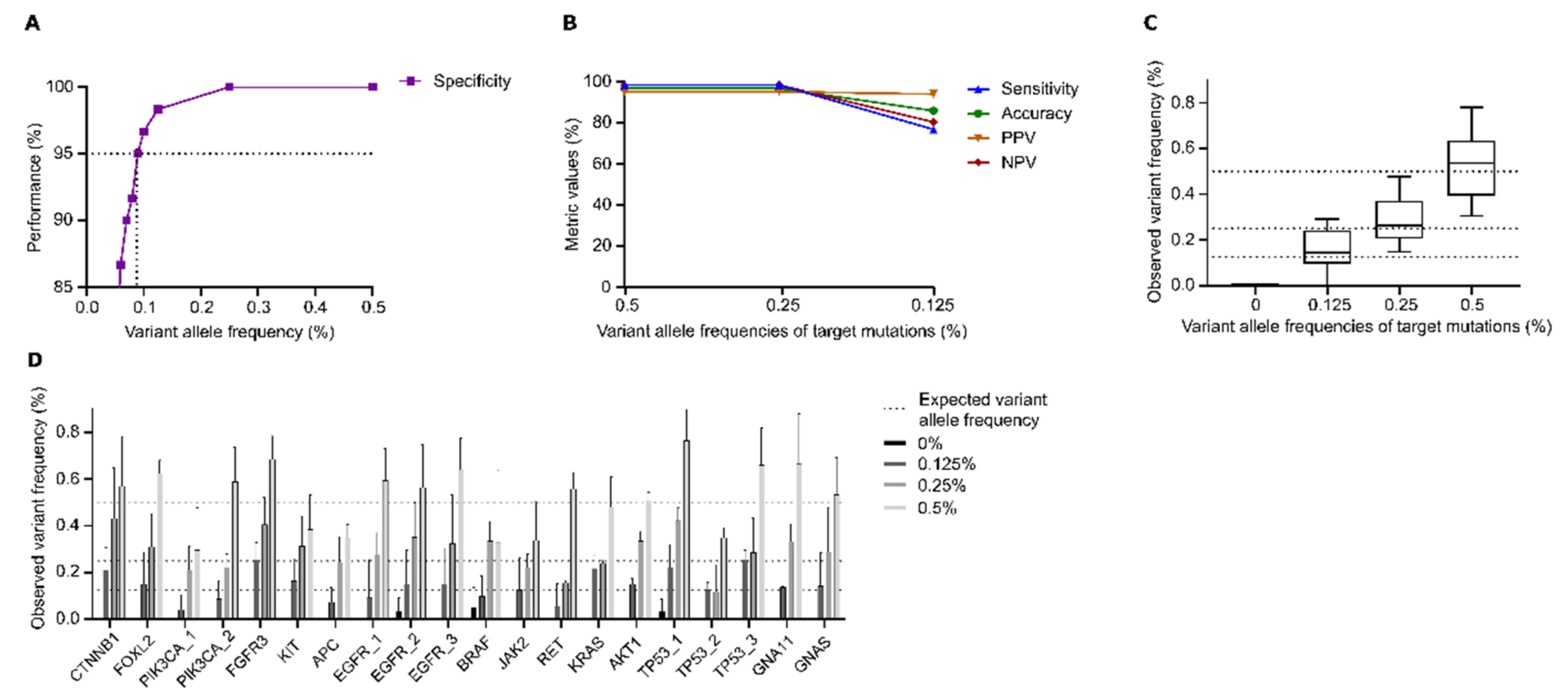
Genes, Free Full-Text
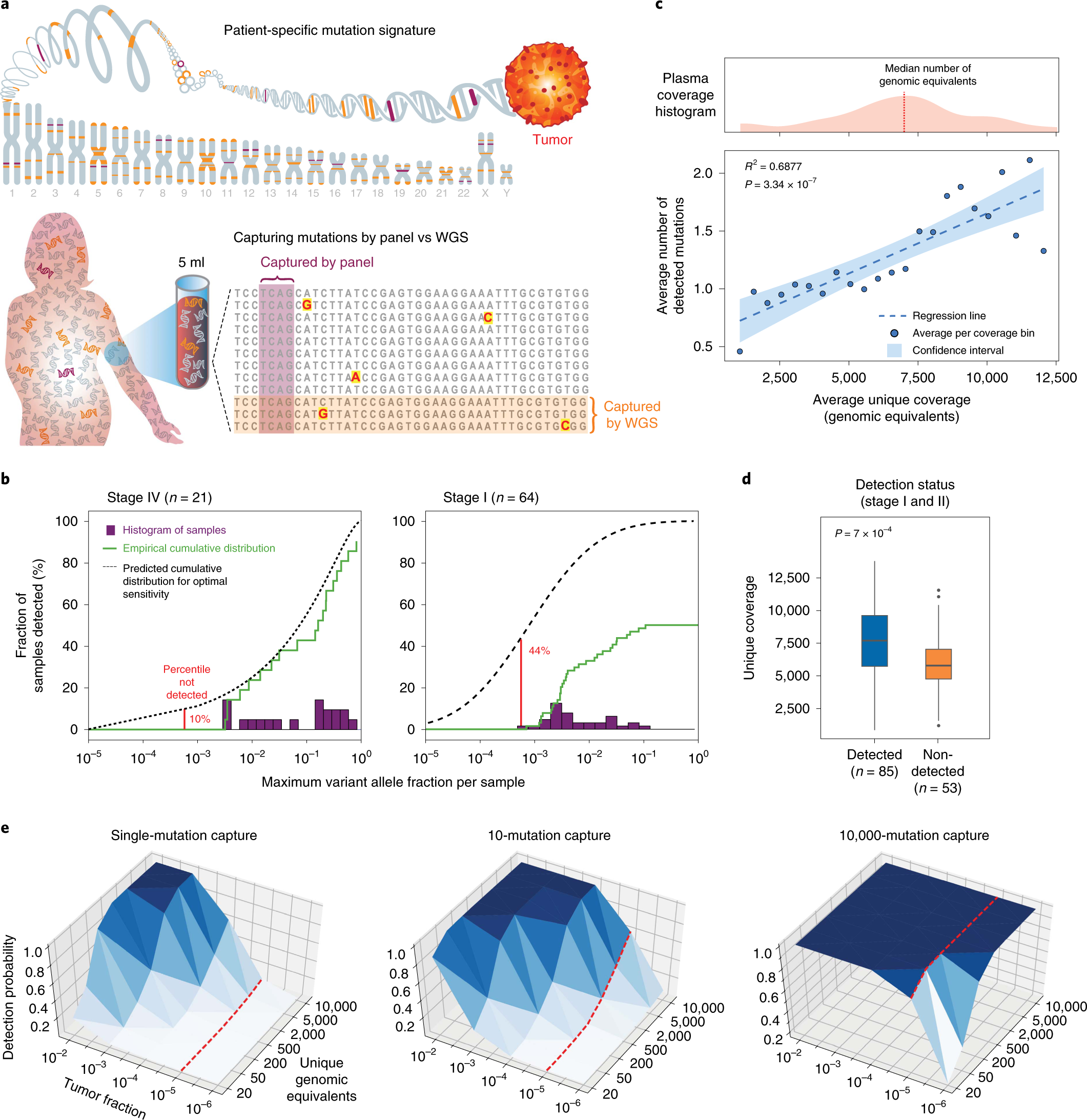
Genome-wide cell-free DNA mutational integration enables ultra

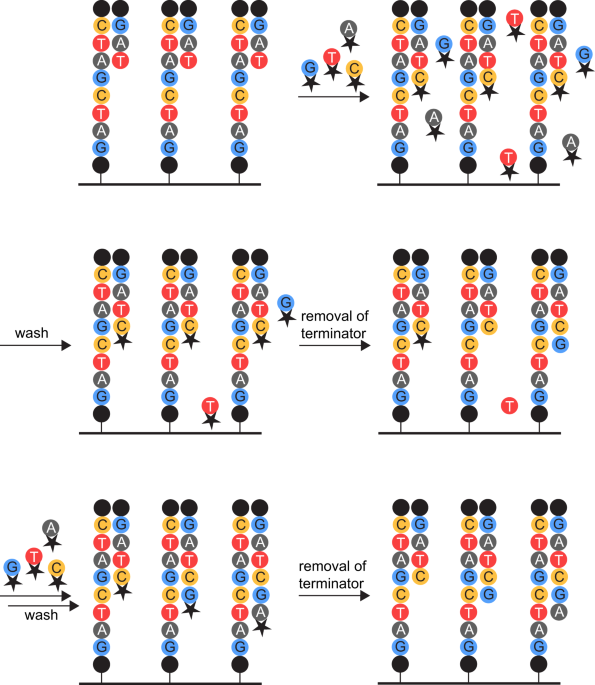
Potential error sources in next-generation sequencing workflow. a
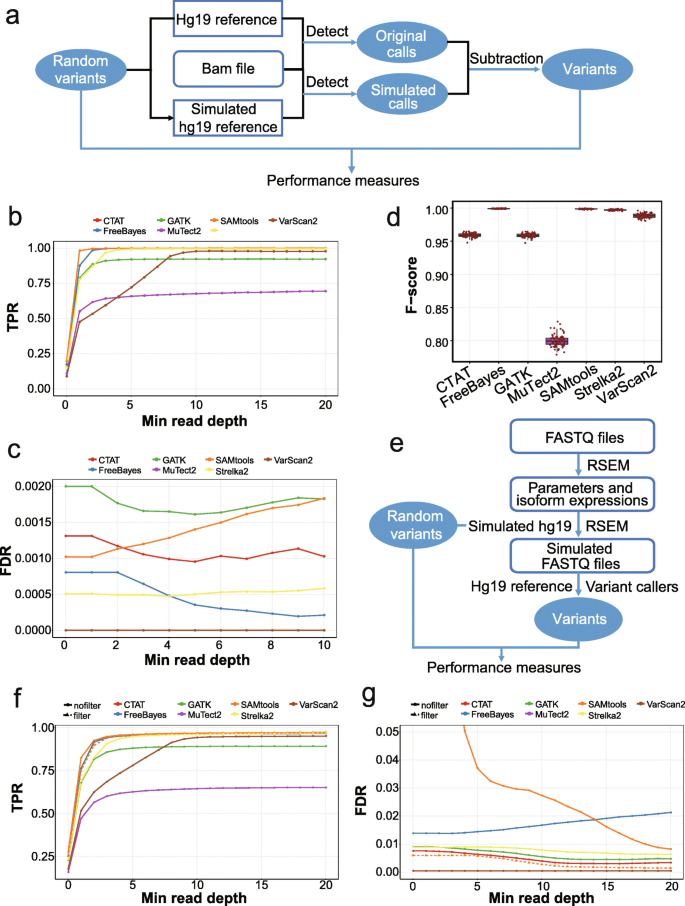
Systematic comparative analysis of single-nucleotide variant

Machine learning-based genome-wide interrogation of somatic copy
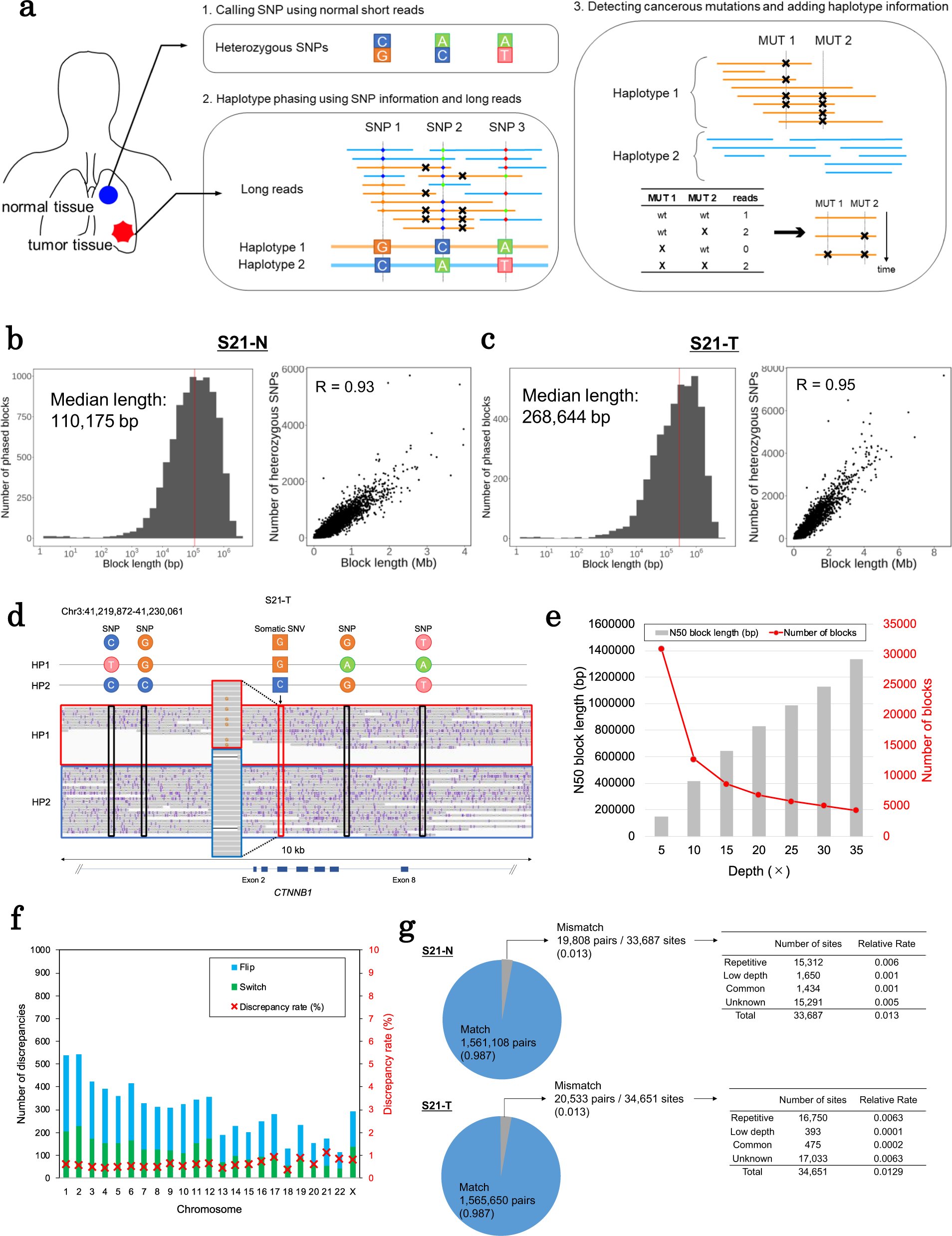
Phasing analysis of lung cancer genomes using a long read
PDF) DREAMS: deep read-level error model for sequencing data
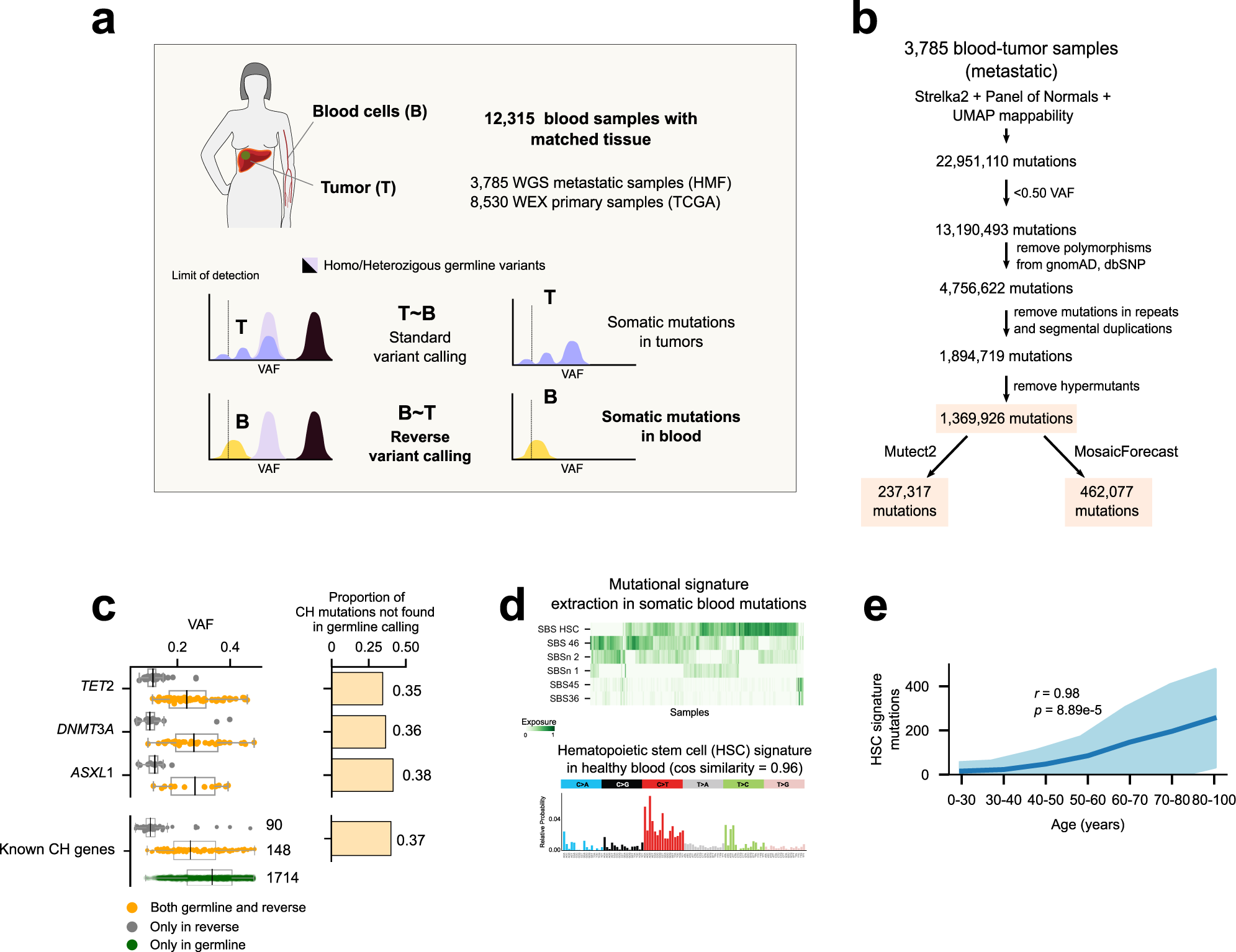
Discovering the drivers of clonal hematopoiesis

Machine learning guided signal enrichment for ultrasensitive
Recomendado para você
-
 The Based God - SCP Foundation28 março 2025
The Based God - SCP Foundation28 março 2025 -
 Gooey Earrings - Drawception28 março 2025
Gooey Earrings - Drawception28 março 2025 -
scp #scpshowerthoughts #minecraft #minecraftparkour #scp173 #scpsecre28 março 2025
-
 Banging on the Door, SCP Foundation28 março 2025
Banging on the Door, SCP Foundation28 março 2025 -
 S I M P SCP Foundation (RP) Amino28 março 2025
S I M P SCP Foundation (RP) Amino28 março 2025 -
 watched rick and morty thought of this SCP - Imgflip28 março 2025
watched rick and morty thought of this SCP - Imgflip28 março 2025 -
 Keyholes hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy28 março 2025
Keyholes hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy28 março 2025 -
 scpwiki28 março 2025
scpwiki28 março 2025 -
Miscellaneous SCPs, SCP Meta Wiki28 março 2025
-
 Inhibition of HIV-1 Replication and Activation of RNase L by Phosphorothioate/Phosphodiester 2′,5′-Oligoadenylate Derivatives - ScienceDirect28 março 2025
Inhibition of HIV-1 Replication and Activation of RNase L by Phosphorothioate/Phosphodiester 2′,5′-Oligoadenylate Derivatives - ScienceDirect28 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Shao Kahn Fan Casting28 março 2025
Shao Kahn Fan Casting28 março 2025 -
 Pronomes28 março 2025
Pronomes28 março 2025 -
 Maa the synonyms of Sacrifice - Make Your Mother Smile28 março 2025
Maa the synonyms of Sacrifice - Make Your Mother Smile28 março 2025 -
 Coding with Scratch - Logging into your Scratch Student Account - scratch.mit.edu28 março 2025
Coding with Scratch - Logging into your Scratch Student Account - scratch.mit.edu28 março 2025 -
 Only Let Yourself Make New Mistakes28 março 2025
Only Let Yourself Make New Mistakes28 março 2025 -
 640+ Branca De Neve Ilustração de stock, gráficos vetoriais e28 março 2025
640+ Branca De Neve Ilustração de stock, gráficos vetoriais e28 março 2025 -
SparkChess - Official game in the Microsoft Store28 março 2025
-
 Tomo-chan Wa Onnanoko! Capítulo 47 - Novel Cool - Lee novelas28 março 2025
Tomo-chan Wa Onnanoko! Capítulo 47 - Novel Cool - Lee novelas28 março 2025 -
 rs Life 2 Download - GameFabrique28 março 2025
rs Life 2 Download - GameFabrique28 março 2025 -
 Be The One - Find Your Home - Hillsborough County SO28 março 2025
Be The One - Find Your Home - Hillsborough County SO28 março 2025