Syndecan-3 is selectively pro-inflammatory in the joint and contributes to antigen-induced arthritis in mice, Arthritis Research & Therapy
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 março 2025
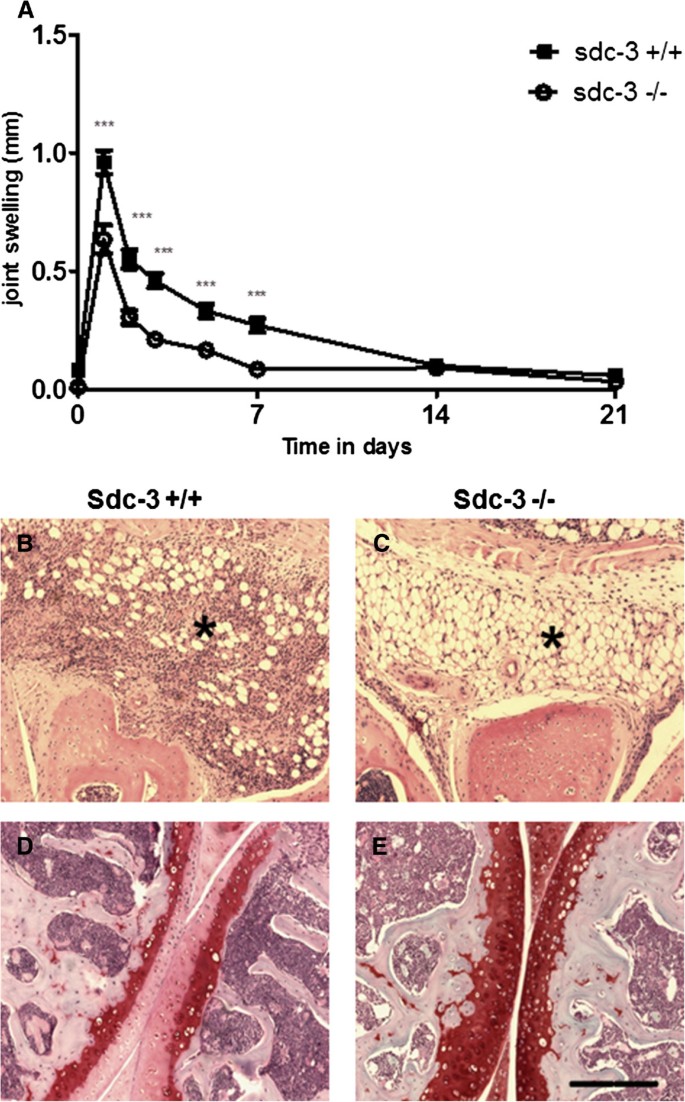
Introduction Syndecans are heparan sulphate proteoglycans expressed by endothelial cells. Syndecan-3 is expressed by synovial endothelial cells of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients where it binds chemokines, suggesting a role in leukocyte trafficking. The objective of the current study was to examine the function of syndecan-3 in joint inflammation by genetic deletion in mice and compare with other tissues. Methods Chemokine C-X-C ligand 1 (CXCL1) was injected in the joints of syndecan-3−/−and wild-type mice and antigen-induced arthritis performed. For comparison chemokine was administered in the skin and cremaster muscle. Intravital microscopy was performed in the cremaster muscle. Results Administration of CXCL1 in knee joints of syndecan-3−/−mice resulted in reduced neutrophil accumulation compared to wild type. This was associated with diminished presence of CXCL1 at the luminal surface of synovial endothelial cells where this chemokine clustered and bound to heparan sulphate. Furthermore, in the arthritis model syndecan-3 deletion led to reduced joint swelling, leukocyte accumulation, cartilage degradation and overall disease severity. Conversely, CXCL1 administration in the skin of syndecan-3 null mice provoked increased neutrophil recruitment and was associated with elevated luminal expression of E-selectin by dermal endothelial cells. Similarly in the cremaster, intravital microscopy showed increased numbers of leukocytes adhering and rolling in venules in syndecan-3−/−mice in response to CXCL1 or tumour necrosis factor alpha. Conclusions This study shows a novel role for syndecan-3 in inflammation. In the joint it is selectively pro-inflammatory, functioning in endothelial chemokine presentation and leukocyte recruitment and cartilage damage in an RA model. Conversely, in skin and cremaster it is anti-inflammatory.

Syndecans Circulation Research

Secondary structure prediction of syndecan-3 core protein. N-terminal

Sarcococca saligna Hydroalcoholic Extract Ameliorates Arthritis in Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Arthritic Rats via Modulation of Inflammatory Biomarkers and Suppression of Oxidative Stress Markers
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Cartilage extracellular matrix-derived matrikines in osteoarthritis
Inflammation-related pyroptosis, a novel programmed cell death pathway, and its crosstalk with immune therapy in cancer treatment
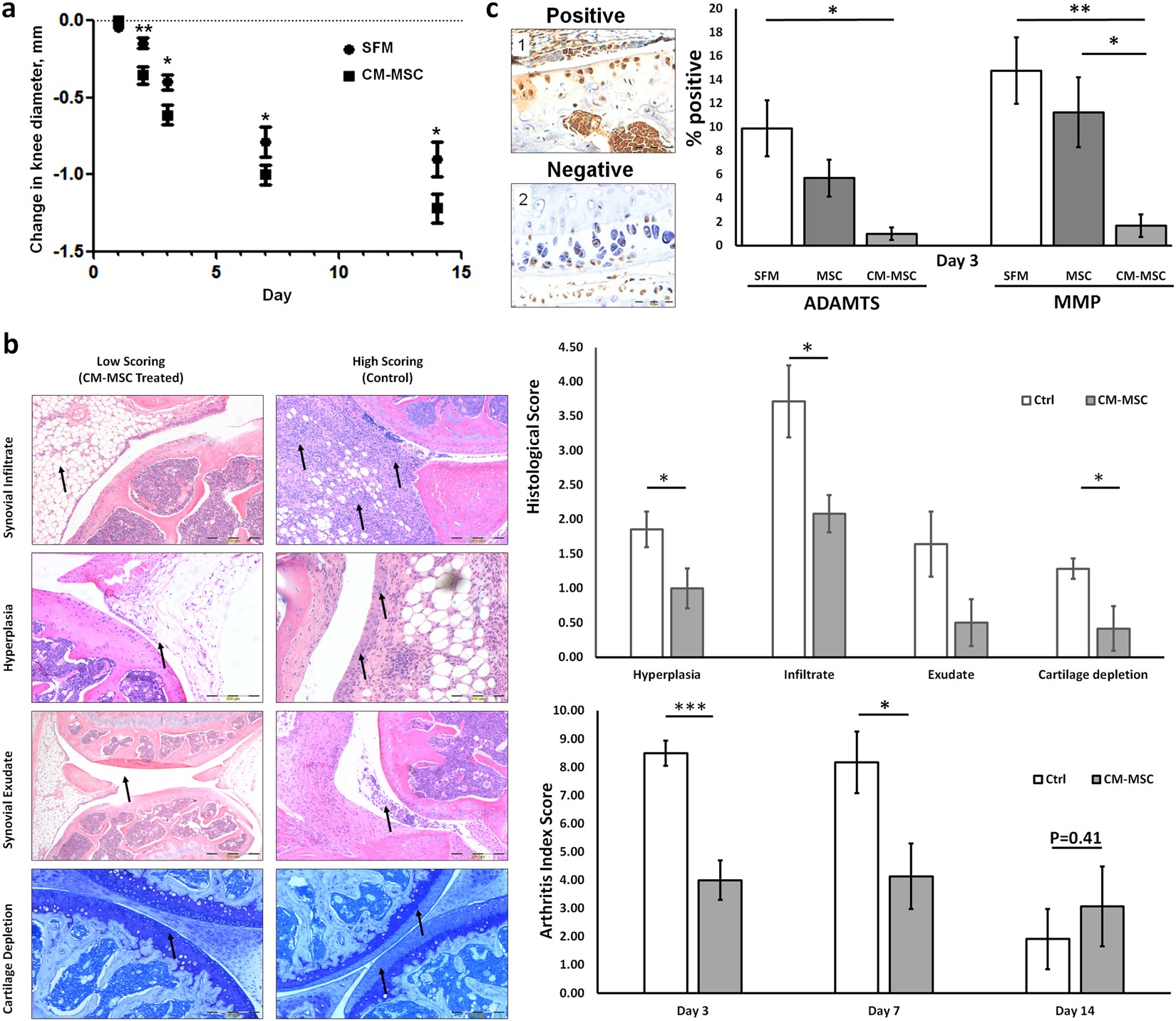
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Reduces Disease Severity and Immune Responses in Inflammatory Arthritis

Synoviocyte-targeted therapy synergizes with TNF inhibition in arthritis reversal

The Anti-Inflammatory Fungal Compound (S)-Curvularin Reduces Proinflammatory Gene Expression in an In Vivo Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis
DNMT3B decreases extracellular matrix degradation and alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration through TRPA1 methylation to inhibit the COX2/YAP axis
Redox regulation of PTPN22 affects the severity of T-cell-dependent autoimmune inflammation
Syndecan-3 regulates MSC adhesion, ERK and AKT signalling in vitro and its deletion enhances MSC efficacy in a model of inflammatory arthritis in vivo
Recomendado para você
-
 Snuff Movies Watch Online Extreme Disturbing Fucked Up28 março 2025
Snuff Movies Watch Online Extreme Disturbing Fucked Up28 março 2025 -
 The Two Popes - Wikipedia28 março 2025
The Two Popes - Wikipedia28 março 2025 -
 MDPOPE on Music Unlimited28 março 2025
MDPOPE on Music Unlimited28 março 2025 -
 Persona - Single - Album by This Is Me Breathing - Apple Music28 março 2025
Persona - Single - Album by This Is Me Breathing - Apple Music28 março 2025 -
 The Waiting Shed on X: Most Disturbed Person on Planet Earth I and II This tweet is a marker that I'm finally done with the second one (over 3 hours long). Mostly28 março 2025
The Waiting Shed on X: Most Disturbed Person on Planet Earth I and II This tweet is a marker that I'm finally done with the second one (over 3 hours long). Mostly28 março 2025 -
mdpope 1 explain|TikTok Search28 março 2025
-
 L'Auberge Espagnole - 2 DVD - Romain Duris - Cecile Of France - Judith Godrèche28 março 2025
L'Auberge Espagnole - 2 DVD - Romain Duris - Cecile Of France - Judith Godrèche28 março 2025 -
 Wai-Kwan Alfred Yung MD Anderson Cancer Center28 março 2025
Wai-Kwan Alfred Yung MD Anderson Cancer Center28 março 2025 -
 Most Disturbed Person On Planet Earth - MDPOPE 3 - Revisão Completa Do Filme28 março 2025
Most Disturbed Person On Planet Earth - MDPOPE 3 - Revisão Completa Do Filme28 março 2025 -
 Exhumation – Song by MDPOPE – Apple Music28 março 2025
Exhumation – Song by MDPOPE – Apple Music28 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 O prodígio da vez na NBA nem sequer estreou na liga28 março 2025
O prodígio da vez na NBA nem sequer estreou na liga28 março 2025 -
GitHub - cybersimple/XSStrike: XSStrike is a program which can crawl, fuzz and bruteforce parameters for XSS. It can also detect and bypass WAFs.28 março 2025
-
![Yes! Precure 5 GoGo [PTP] by JellyHeartsArchive on DeviantArt](https://images-wixmp-ed30a86b8c4ca887773594c2.wixmp.com/f/f69dcefb-5025-4726-a70a-45c90476cb1b/dd1od3m-e0e0f6b6-2621-411f-bee7-f342bf35e378.png?token=eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJ1cm46YXBwOjdlMGQxODg5ODIyNjQzNzNhNWYwZDQxNWVhMGQyNmUwIiwiaXNzIjoidXJuOmFwcDo3ZTBkMTg4OTgyMjY0MzczYTVmMGQ0MTVlYTBkMjZlMCIsIm9iaiI6W1t7InBhdGgiOiJcL2ZcL2Y2OWRjZWZiLTUwMjUtNDcyNi1hNzBhLTQ1YzkwNDc2Y2IxYlwvZGQxb2QzbS1lMGUwZjZiNi0yNjIxLTQxMWYtYmVlNy1mMzQyYmYzNWUzNzgucG5nIn1dXSwiYXVkIjpbInVybjpzZXJ2aWNlOmZpbGUuZG93bmxvYWQiXX0.Nc0TOpTs1ZDrr3_3eJSh7sXO7GbO2LMvetrxKSOxzE4) Yes! Precure 5 GoGo [PTP] by JellyHeartsArchive on DeviantArt28 março 2025
Yes! Precure 5 GoGo [PTP] by JellyHeartsArchive on DeviantArt28 março 2025 -
 Maximum ELO rating of 30 best players of all time28 março 2025
Maximum ELO rating of 30 best players of all time28 março 2025 -
 Golden State Warriors close out Boston Celtics to win fourth NBA28 março 2025
Golden State Warriors close out Boston Celtics to win fourth NBA28 março 2025 -
 The Women of Fullmetal Alchemist: Brotherhood – Just Something28 março 2025
The Women of Fullmetal Alchemist: Brotherhood – Just Something28 março 2025 -
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_19863d4200d245c3a2ff5b383f548bb6/internal_photos/bs/2023/E/J/tsS9DjQJu2t5SSLgt3AQ/img-5591.jpg) Penteados para bebês: dicas, cuidados e ideias para estilizar o cabelo das crianças28 março 2025
Penteados para bebês: dicas, cuidados e ideias para estilizar o cabelo das crianças28 março 2025 -
 Bola de batida poderosa com efeito de trilha de fogo do jogador de28 março 2025
Bola de batida poderosa com efeito de trilha de fogo do jogador de28 março 2025 -
 I was gonna do something on Sonic Speed Simulator but I'll wait a28 março 2025
I was gonna do something on Sonic Speed Simulator but I'll wait a28 março 2025 -
 Aprenda a fazer bolos de pote e os transforme em renda extra28 março 2025
Aprenda a fazer bolos de pote e os transforme em renda extra28 março 2025
