Cnidarian hair cell development illuminates an ancient role for the class IV POU transcription factor in defining mechanoreceptor identity
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 29 março 2025
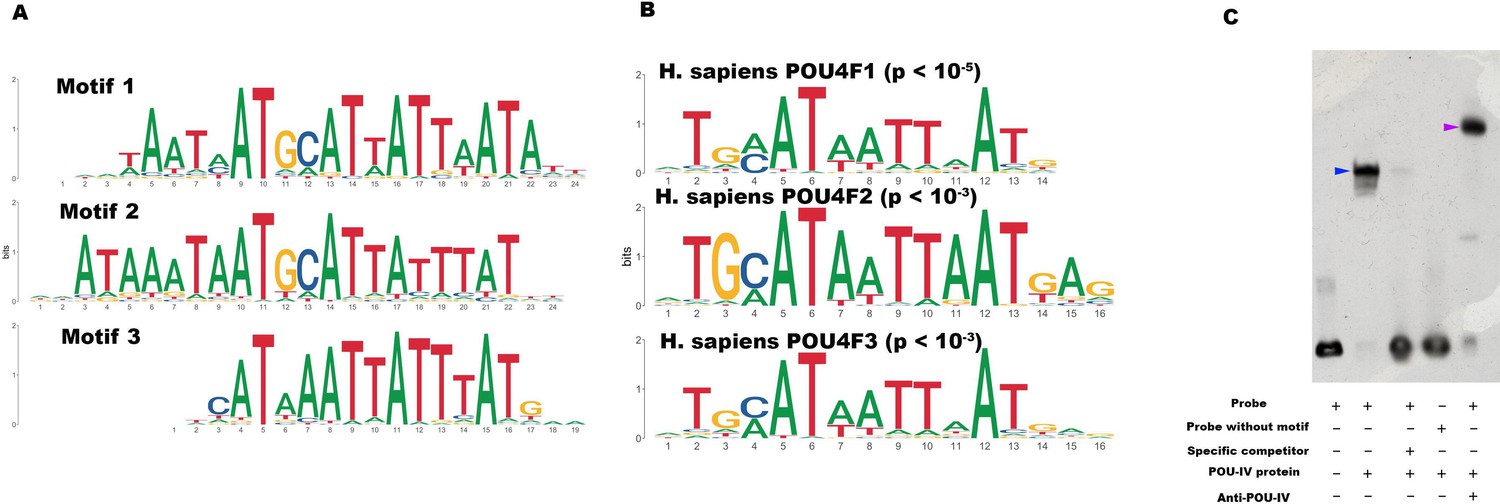
Developmental genetics of sea anemone mechanosensory neurons provides insights into the deep evolutionary history of mechanoreceptor development in animals.

PDF) Cnidarian hair cell development illuminates an ancient role
67-42-5, MFCD00004291, EGTA

Reconstruction of protein domain evolution using single-cell
América Ramírez (@americaramcol) / X
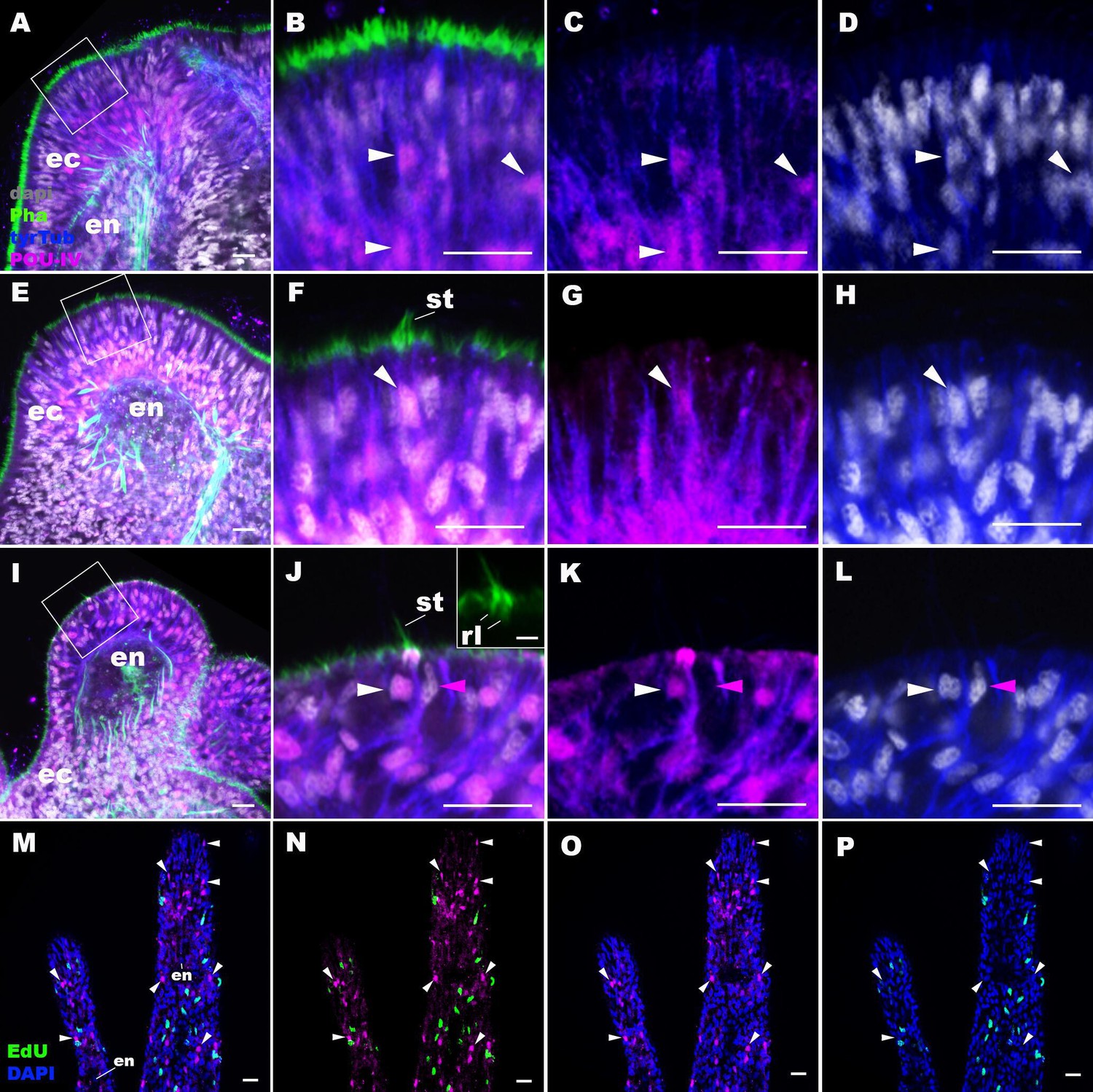
Cnidarian hair cell development illuminates an ancient role for

Publications - Regulatory RNA Lab

Brn3/POU‐IV‐type POU homeobox genes—Paradigmatic regulators of

Polycystin-1 Induces Cell Migration by Regulating

Cnidarian hair cell development illuminates an ancient role for

Single-cell transcriptomics identifies conserved regulators of

Transcription factors with conserved binding sites near ATOH1 on
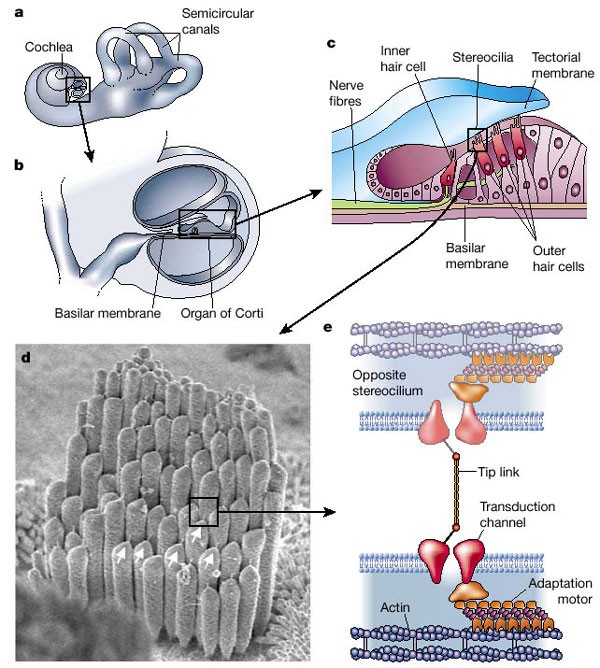
Molecular basis of mechanosensory transduction

Transcription factor AP2 controls cnidarian germ cell induction

PDF] Diversity of cilia-based mechanosensory systems and their
Recomendado para você
-
pou #sigma #foryou #fyp29 março 2025
-
 Pou, UnAnything Wiki29 março 2025
Pou, UnAnything Wiki29 março 2025 -
 New Event – Konbit Pou Potapiman29 março 2025
New Event – Konbit Pou Potapiman29 março 2025 -
 Both Oct-1 POU and λ cI activate transcription by recruiting a core29 março 2025
Both Oct-1 POU and λ cI activate transcription by recruiting a core29 março 2025 -
 roupa do pou29 março 2025
roupa do pou29 março 2025 -
Arnau Pou Photography29 março 2025
-
 CapCut_sound pou viral tuut tut tut tut29 março 2025
CapCut_sound pou viral tuut tut tut tut29 março 2025 -
![PDF] Implementing Lean Six Sigma into curriculum design and delivery – a case study in higher education](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0c293702fba56f5014342e33639779cc7b2162c5/25-Table2-1.png) PDF] Implementing Lean Six Sigma into curriculum design and delivery – a case study in higher education29 março 2025
PDF] Implementing Lean Six Sigma into curriculum design and delivery – a case study in higher education29 março 2025 -
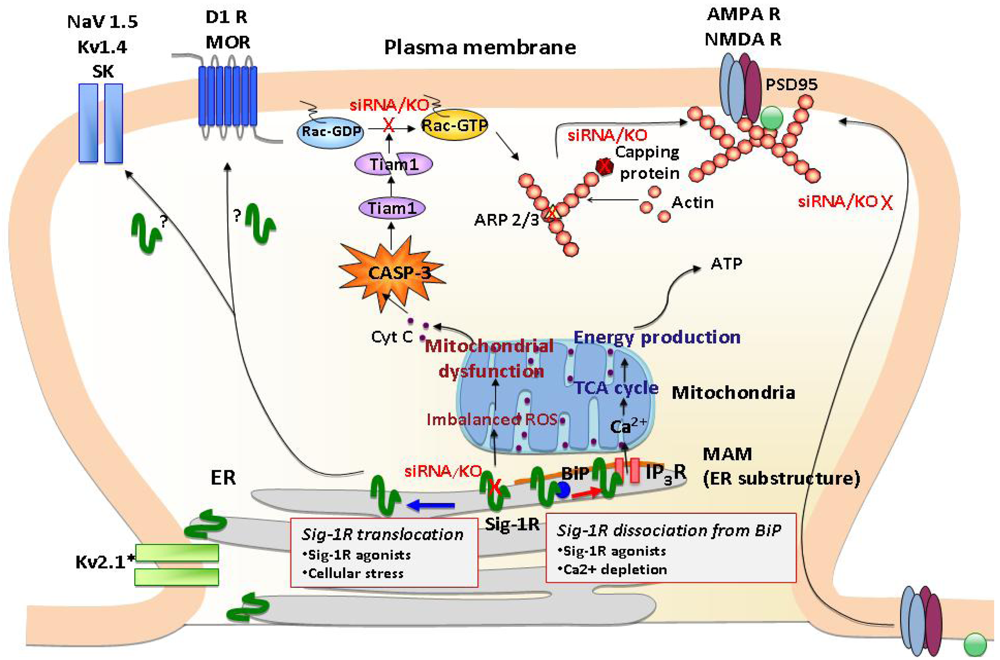 Pharmaceuticals, Free Full-Text29 março 2025
Pharmaceuticals, Free Full-Text29 março 2025 -
 Edigar Tiago GIF - Edigar Tiago Pou - Discover & Share GIFs29 março 2025
Edigar Tiago GIF - Edigar Tiago Pou - Discover & Share GIFs29 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 dfgdfgdf29 março 2025
dfgdfgdf29 março 2025 -
 Stumble Guys Vs Fall Guys29 março 2025
Stumble Guys Vs Fall Guys29 março 2025 -
bomber friends edit|Pesquisa do TikTok29 março 2025
-
 MS GIF Animator - Download29 março 2025
MS GIF Animator - Download29 março 2025 -
 Read Senpai Ga Urusai Kouhai No Hanashi Manga on Mangakakalot29 março 2025
Read Senpai Ga Urusai Kouhai No Hanashi Manga on Mangakakalot29 março 2025 -
South Gama Tattoo - Kimetsu no Yaiba ou Demon Slayer você já assistiu esse anime? A trama mostra um jovem rapaz chamado Tanjiro que trabalha para ajudar sua família composta por uma29 março 2025
-
Gacha Online is an unpleasant drug trip sometimes 😟29 março 2025
-
 How to install NOOBS Lite and RISC OS on your Raspberry Pi 329 março 2025
How to install NOOBS Lite and RISC OS on your Raspberry Pi 329 março 2025 -
Extreme Moto Peças 62 3259-035229 março 2025
-
 Kakegurui Twin - Zerochan Anime Image Board29 março 2025
Kakegurui Twin - Zerochan Anime Image Board29 março 2025





