(PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 06 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features and variants in both the CREBBP and EP300 genes: a case report, BMC Medical Genetics

Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo‐Ngongang - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library

PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly

PDF) Generation of the Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome type 2 patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cell line (IAIi001-A) carrying the EP300 exon 23 stop mutation c.3829A > T, p.(Lys1277*)
Case report: a Chinese girl like atypical Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome caused by a novel heterozygous mutation of the EP300 gene, BMC Medical Genomics
A novel de novo MTOR gain-of-function variant in a patient with Smith-Kingsmore syndrome and Antiphospholipid syndrome
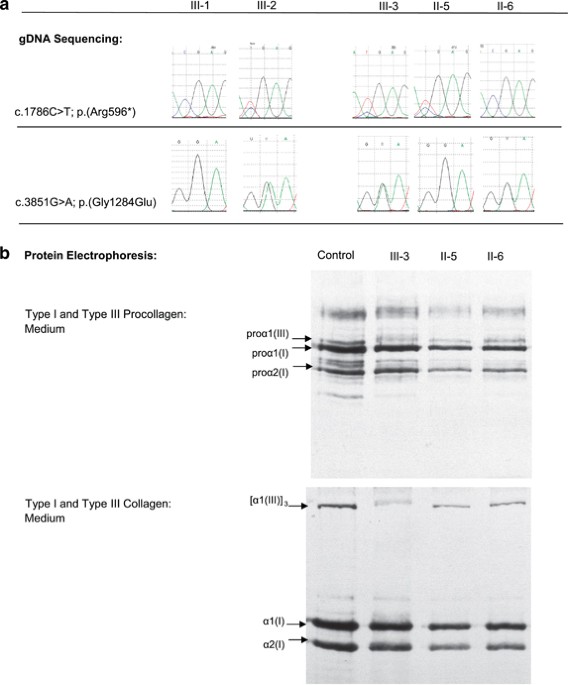
Vascular Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome in siblings with biallelic COL3A1 sequence variants and marked clinical variability in the extended family
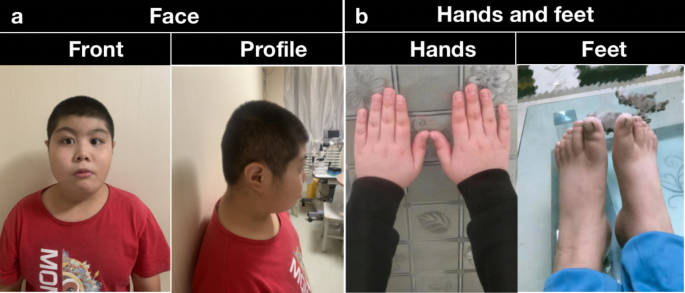
De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia, BMC Medical Genomics
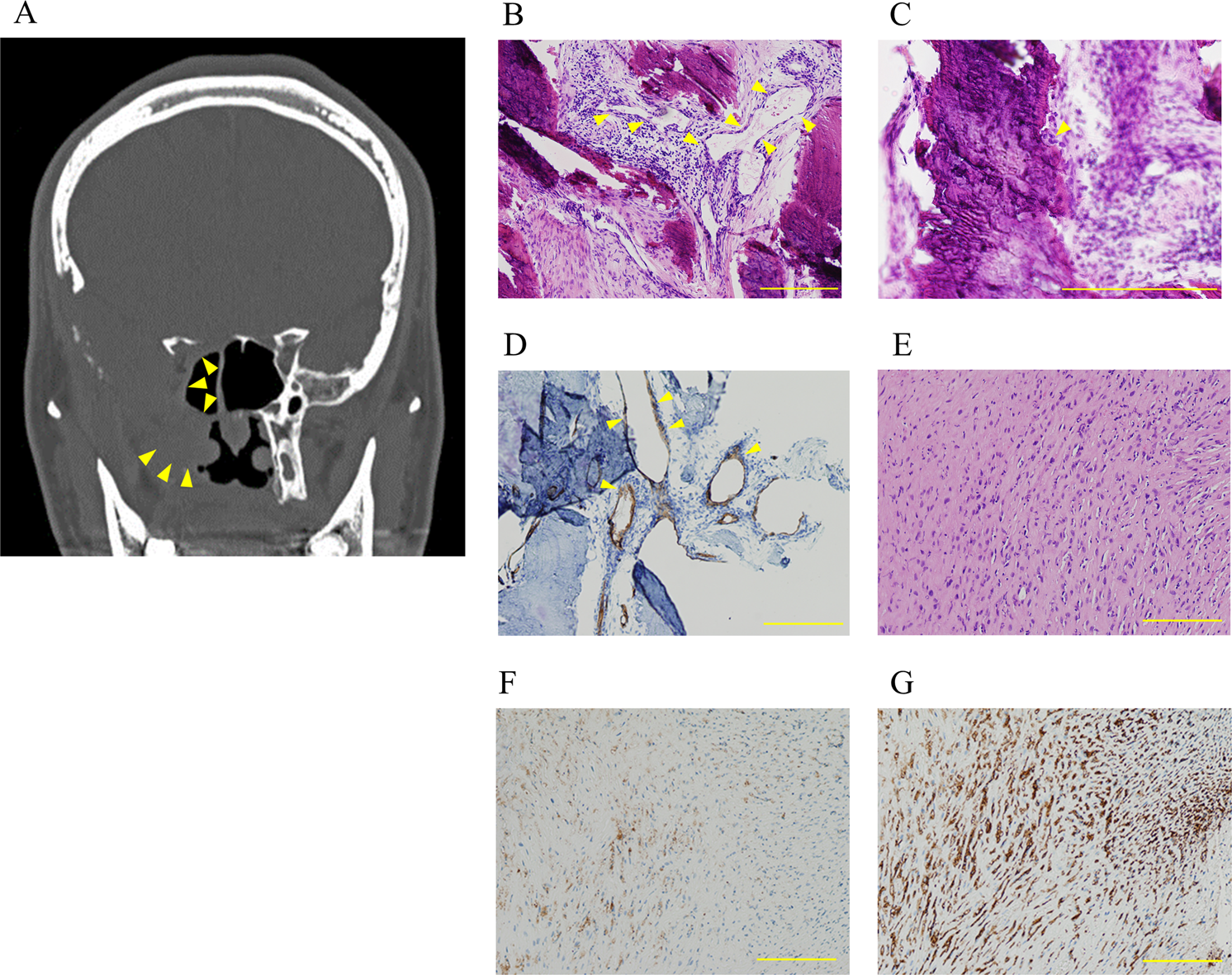
A somatic activating KRAS variant identified in an affected lesion of a patient with Gorham–Stout disease
PDF) Novel heterozygous variants in the EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2: Reports from two Chinese children
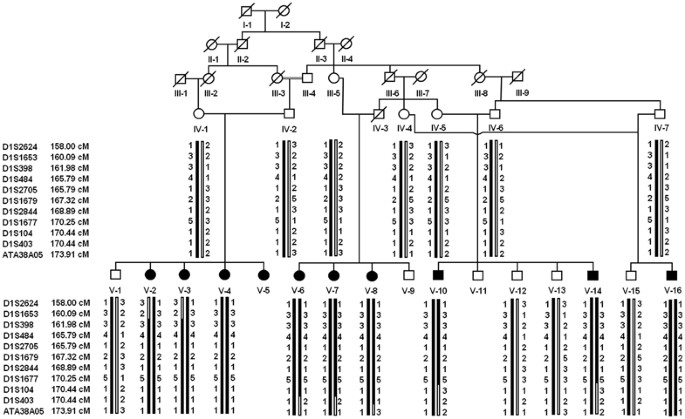
Mutation in PVRL4 gene encoding nectin-4 underlies ectodermal-dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome (EDSS1)
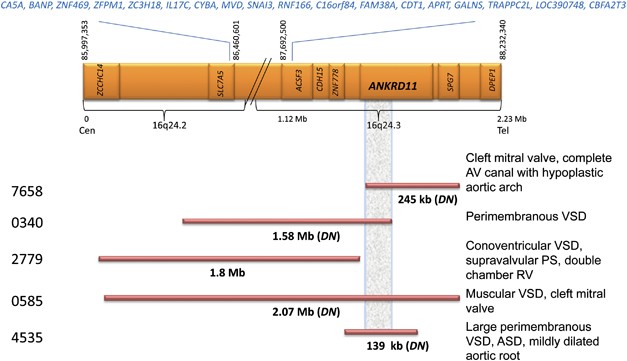
Rare DNA copy number variants in cardiovascular malformations with extracardiac abnormalities

Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP300
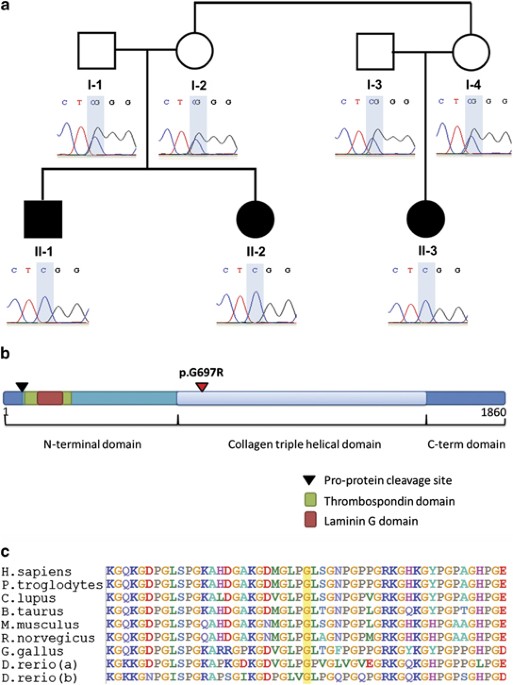
Mutations in COL27A1 cause Steel syndrome and suggest a founder mutation effect in the Puerto Rican population
Recomendado para você
-
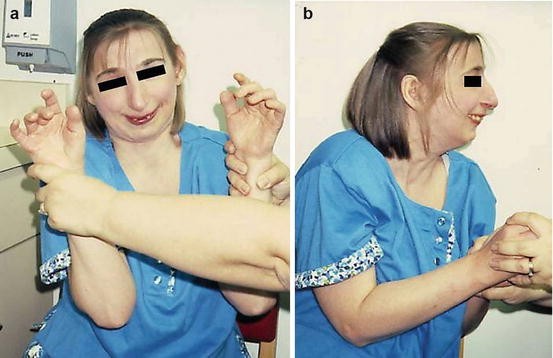 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome06 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome06 abril 2025 -
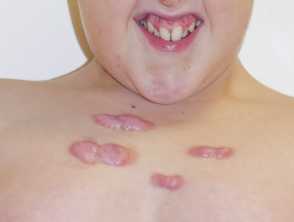 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A Complete Overview — DermNet06 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A Complete Overview — DermNet06 abril 2025 -
![Figure 2. [Broad terminal phalanges (A) and broad, radially deviated thumbs (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1526/bin/rsts-Image002.jpg) Figure 2. [Broad terminal phalanges (A) and broad, radially deviated thumbs (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf06 abril 2025
Figure 2. [Broad terminal phalanges (A) and broad, radially deviated thumbs (B)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf06 abril 2025 -
 The novel and recurrent variants in exon 31 of CREBBP in Japanese patients with Menke–Hennekam syndrome - Nishi - 2022 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library06 abril 2025
The novel and recurrent variants in exon 31 of CREBBP in Japanese patients with Menke–Hennekam syndrome - Nishi - 2022 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library06 abril 2025 -
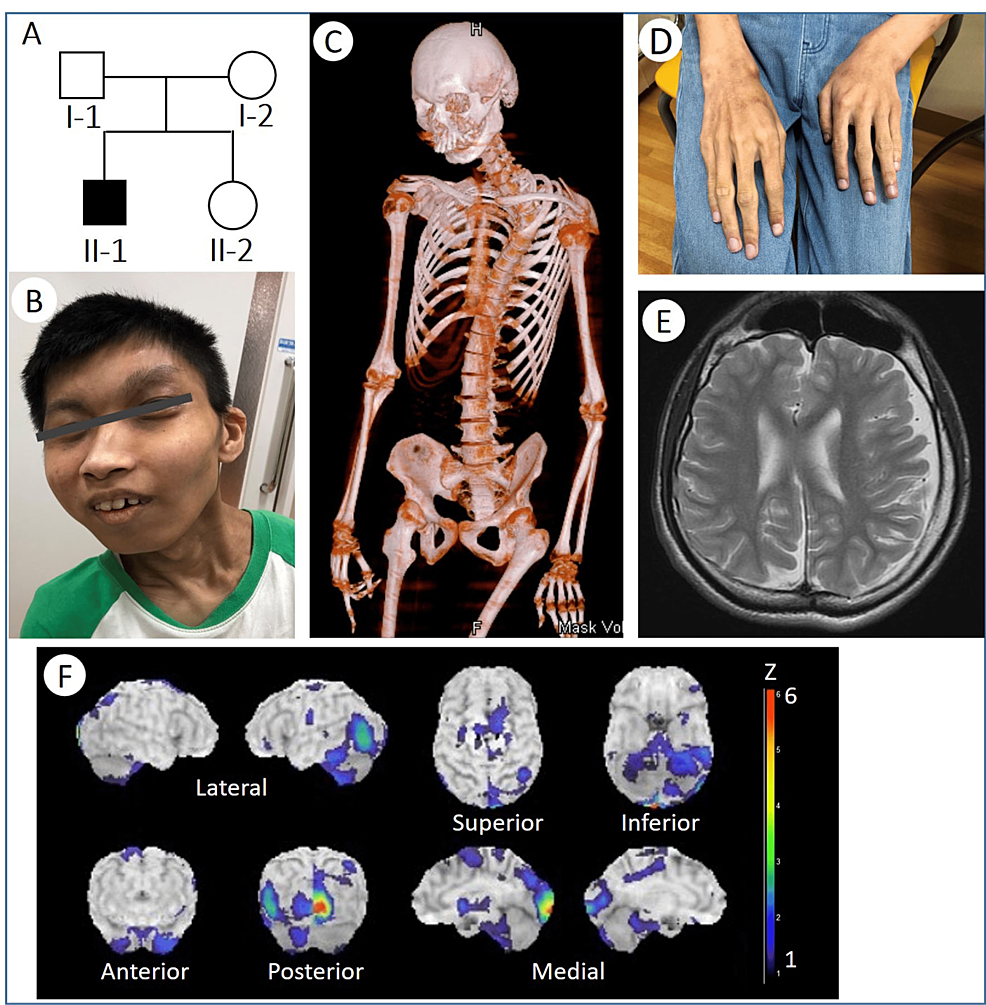 Cureus, Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified a Novel DYRK1A Variant in a Patient With Intellectual Developmental Disorder, Autosomal Dominant 706 abril 2025
Cureus, Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified a Novel DYRK1A Variant in a Patient With Intellectual Developmental Disorder, Autosomal Dominant 706 abril 2025 -
 Silver Russell Syndrome: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews06 abril 2025
Silver Russell Syndrome: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews06 abril 2025 -
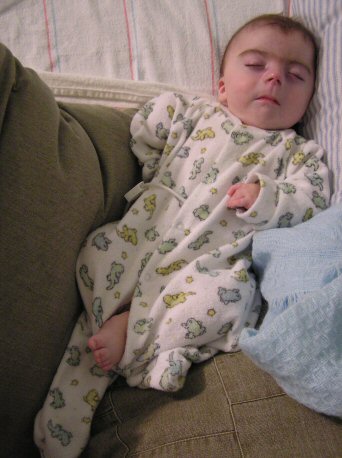 What is CdLS? Ben and his Brothers: Life with 4 boys and CdLS06 abril 2025
What is CdLS? Ben and his Brothers: Life with 4 boys and CdLS06 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo06 abril 2025
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo06 abril 2025 -
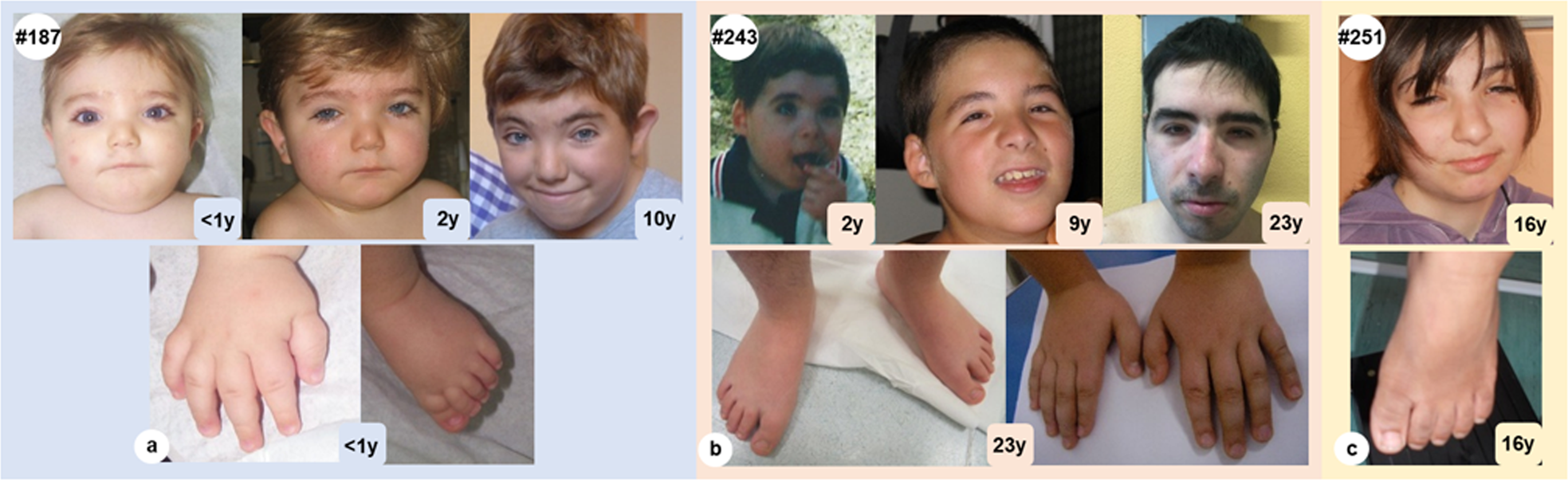 Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping06 abril 2025
Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping06 abril 2025 -
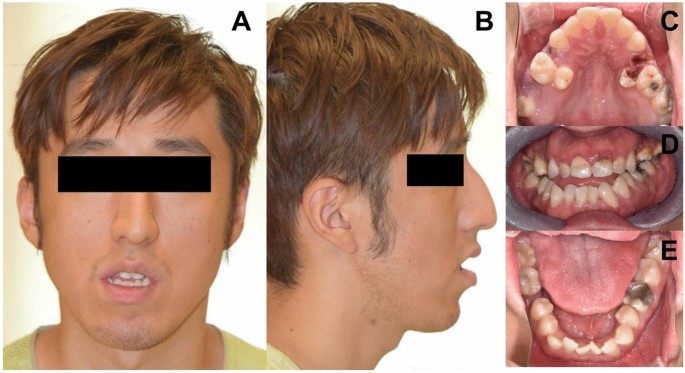 Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient06 abril 2025
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient06 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Não reclame da vida dias ruins são necessários06 abril 2025
Não reclame da vida dias ruins são necessários06 abril 2025 -
 Sonic The Hedgehog Lego Dimensions Level Pack 71244 em Promoção na Americanas06 abril 2025
Sonic The Hedgehog Lego Dimensions Level Pack 71244 em Promoção na Americanas06 abril 2025 -
 Skate De Dedo C/ Rampa Brinquedo Infantil Divertido Original06 abril 2025
Skate De Dedo C/ Rampa Brinquedo Infantil Divertido Original06 abril 2025 -
 Pokémon UNITE Buzzwole vai causar uma derrubada e tanto contra a oposição no Pokémon UNITE06 abril 2025
Pokémon UNITE Buzzwole vai causar uma derrubada e tanto contra a oposição no Pokémon UNITE06 abril 2025 -
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2022/4/7/pzPpYlTAiK3FX0xFDoIQ/capa-4.jpg) Corinthians x Flamengo ao vivo: onde assistir ao jogo da Libertadores online06 abril 2025
Corinthians x Flamengo ao vivo: onde assistir ao jogo da Libertadores online06 abril 2025 -
 Alan Wake's American Nightmare - PCGamingWiki PCGW - bugs, fixes, crashes, mods, guides and improvements for every PC game06 abril 2025
Alan Wake's American Nightmare - PCGamingWiki PCGW - bugs, fixes, crashes, mods, guides and improvements for every PC game06 abril 2025 -
 Assistir Kami Tachi Ni Hirowareta Otoko - Episódio - 4 animes online06 abril 2025
Assistir Kami Tachi Ni Hirowareta Otoko - Episódio - 4 animes online06 abril 2025 -
Anya Brown - Washington, District of Columbia, United States, Professional Profile06 abril 2025
-
 Novidades vindas da Shonen Sunday06 abril 2025
Novidades vindas da Shonen Sunday06 abril 2025 -
 Golden Tulip Borjomi Palace - Borjomi, Georgia Meeting Rooms06 abril 2025
Golden Tulip Borjomi Palace - Borjomi, Georgia Meeting Rooms06 abril 2025
