Metabolic engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans for pinene
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 10 abril 2025
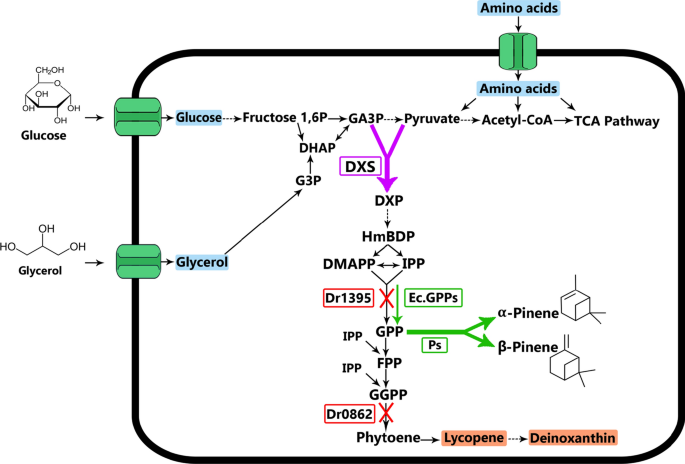
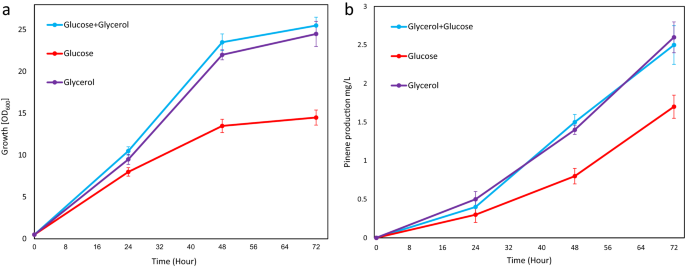
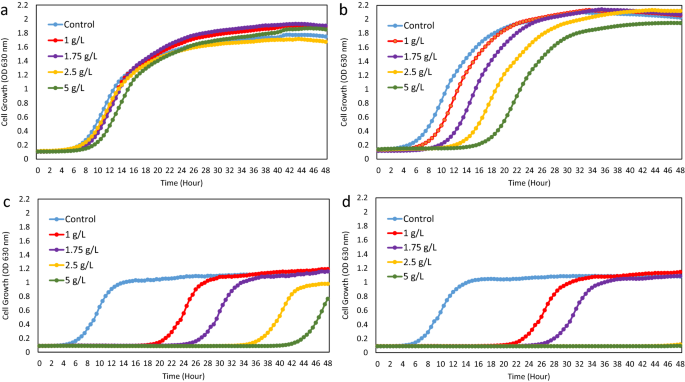
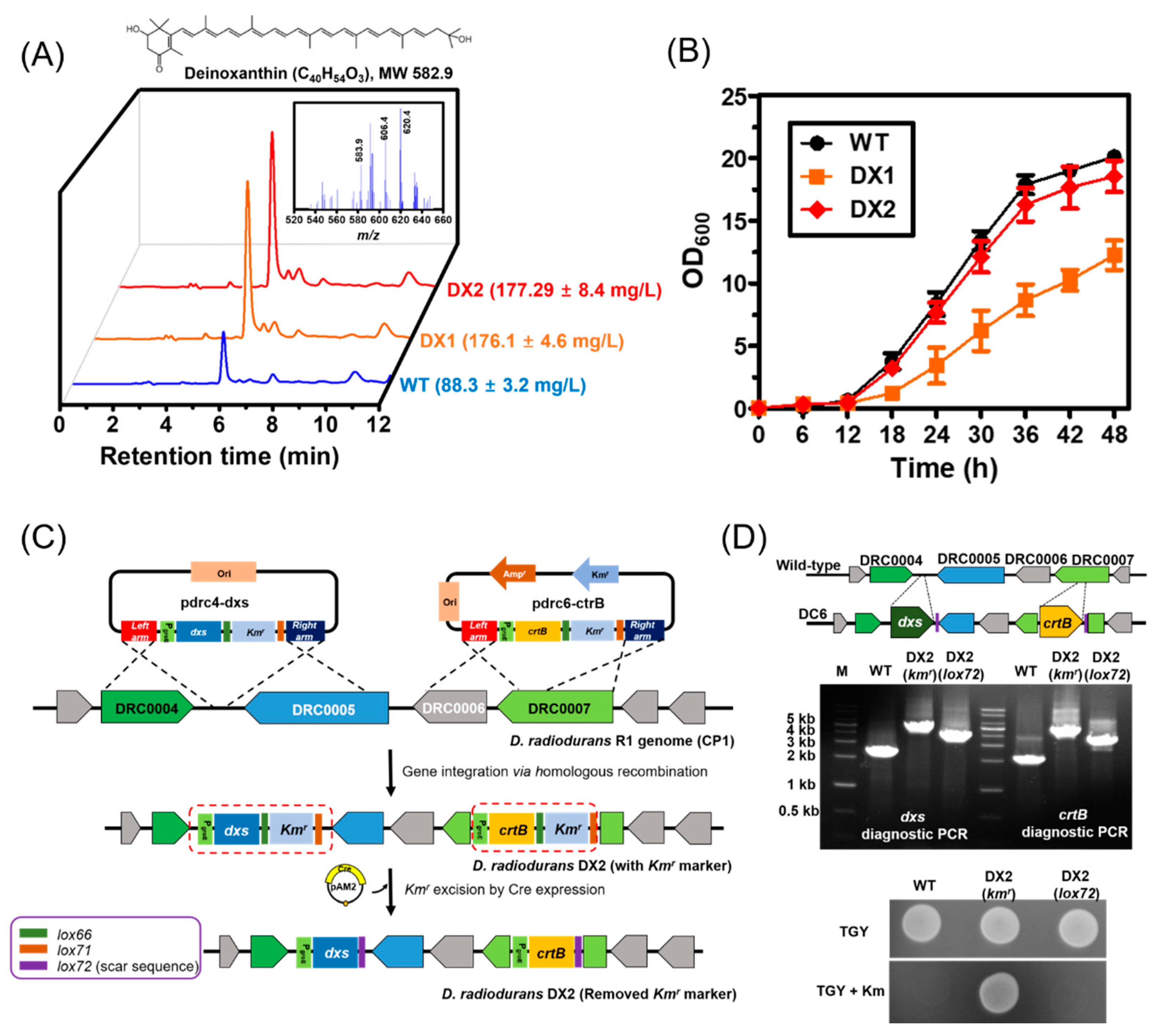
Background The objective of this work was to engineer Deinococcus radiodurans R1 as a microbial cell factory for the production of pinene, a monoterpene molecule prominently used for the production of fragrances, pharmaceutical products, and jet engine biofuels. Our objective was to produce pinene from glycerol, an abundant by-product of various industries. Results To enable pinene production in D. radiodurans, we expressed the pinene synthase from Abies grandis, the geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) synthase from Escherichia coli, and overexpressed the native 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase. Further, we disrupted the deinoxanthin pathway competing for the substrate GPP by either inactivating the gene dr0862, encoding phytoene synthase, or substituting the native GPP synthase with that of E. coli. These manipulations resulted in a D. radiodurans strain capable of producing 3.2 ± 0.2 mg/L pinene in a minimal medium supplemented with glycerol, with a yield of 0.13 ± 0.04 mg/g glycerol in shake flask cultures. Additionally, our results indicated a higher tolerance of D. radiodurans towards pinene as compared to E. coli. Conclusions In this study, we successfully engineered the extremophile bacterium D. radiodurans to produce pinene. This is the first study demonstrating the use of D. radiodurans as a cell factory for the production of terpenoid molecules. Besides, its high resistance to pinene makes D. radiodurans a suitable host for further engineering efforts to increase pinene titer as well as a candidate for the production of the other terpenoid molecules.
Metabolic engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans for pinene production from glycerol, Microbial Cell Factories

Microbial synthesis of pinene.

The schematic of the terpene synthetic pathway and the functional
Metabolic engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans for pinene production from glycerol, Microbial Cell Factories
Microorganisms, Free Full-Text
Proteometabolomic response of Deinococcus radiodurans exposed to UVC and vacuum conditions: Initial studies prior to the Tanpopo space mission
Microbial Cell Factories

Engineering Robustness of Microbial Cell Factories - Gong - 2017 - Biotechnology Journal - Wiley Online Library
Frontiers Deinococcus radiodurans UWO298 Dependence on Background Radiation for Optimal Growth

Accumulation of Mn(II) in Deinococcus radiodurans Facilitates Gamma-Radiation Resistance
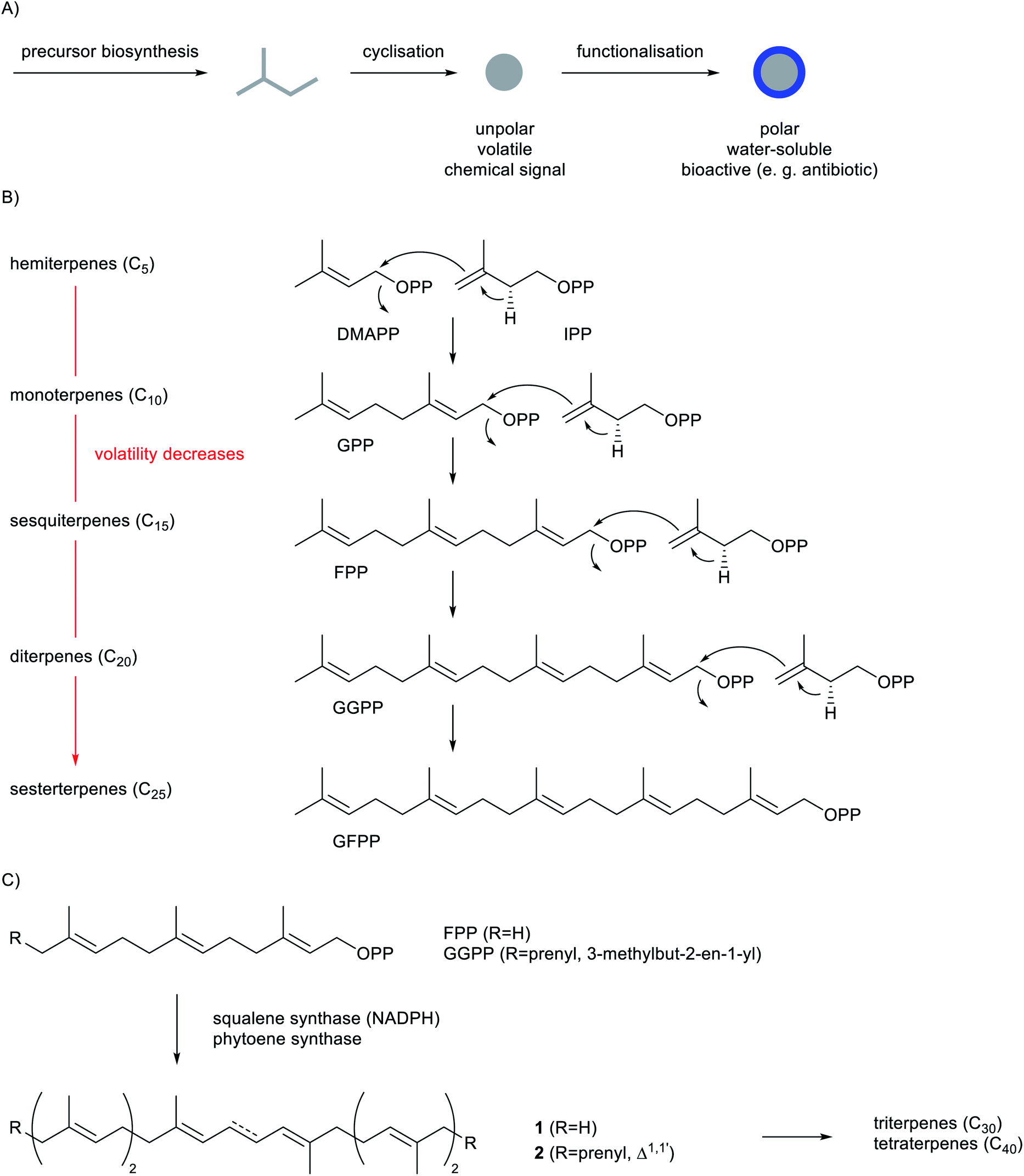
Biosynthesis, evolution and ecology of microbial terpenoids - Natural Product Reports (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1NP00047K

PDF] Metabolic Engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans for the Production of Phytoene.
Toward improved terpenoids biosynthesis: strategies to enhance the capabilities of cell factories, Bioresources and Bioprocessing

A Novel Small RNA, DsrO, in Deinococcus radiodurans Promotes Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase (msrA) Expression for Oxidative Stress Adaptation
Recomendado para você
-
 Microbiology from A to Z explained - Micropia - Micropia10 abril 2025
Microbiology from A to Z explained - Micropia - Micropia10 abril 2025 -
 Deinococcus radiodurans10 abril 2025
Deinococcus radiodurans10 abril 2025 -
 Extremophile organisms: Deinococcus radiodurans. Science blog 12110 abril 2025
Extremophile organisms: Deinococcus radiodurans. Science blog 12110 abril 2025 -
 Deinococcus Radiodurans: The World's Toughest Bacterium. A Review10 abril 2025
Deinococcus Radiodurans: The World's Toughest Bacterium. A Review10 abril 2025 -
 Deinococcus radiodurans ( daviddarling.info10 abril 2025
Deinococcus radiodurans ( daviddarling.info10 abril 2025 -
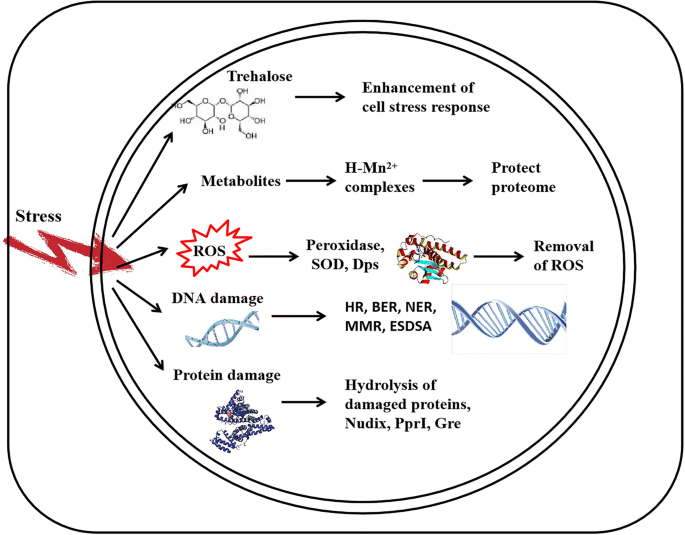 The diversity and commonalities of the radiation-resistance10 abril 2025
The diversity and commonalities of the radiation-resistance10 abril 2025 -
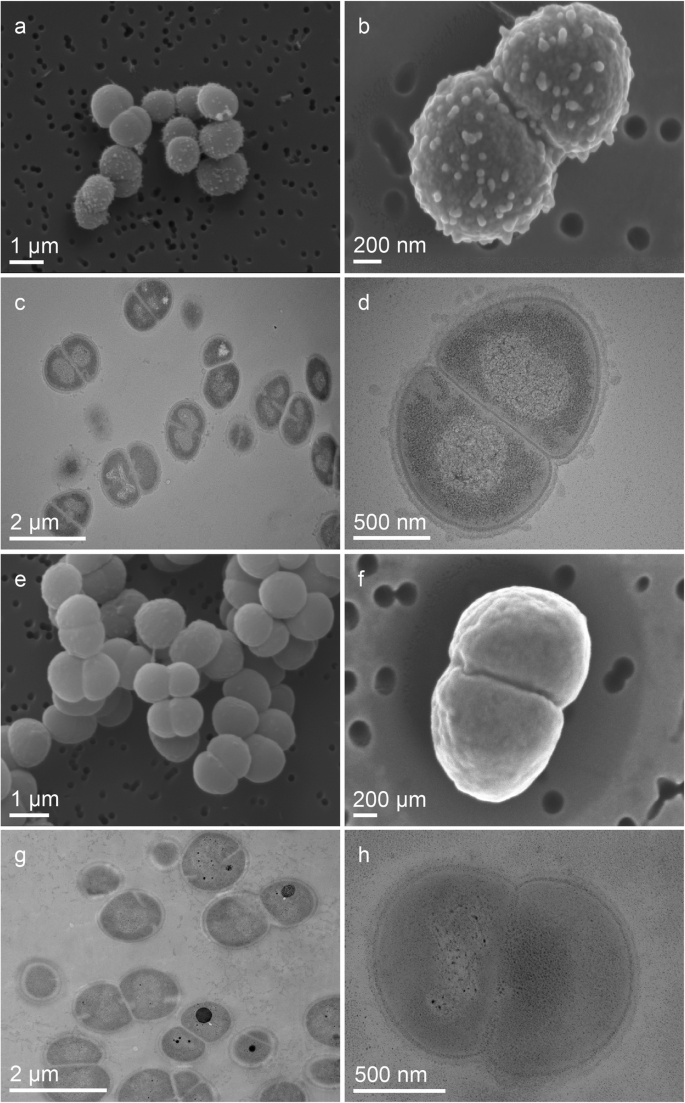 Molecular repertoire of Deinococcus radiodurans after 1 year of10 abril 2025
Molecular repertoire of Deinococcus radiodurans after 1 year of10 abril 2025 -
4C2U: Crystal Structure Of Deinococcus Radiodurans Uvrd In Complex10 abril 2025
-
Deinococcus radiodurans10 abril 2025
-
 Deinococcus radiodurans nucleoid and distribution states of the10 abril 2025
Deinococcus radiodurans nucleoid and distribution states of the10 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/72590116/ARMORED_CORE__VI_FIRES_OF_RUBICON__20230829103124.0.jpg) How to get the Moonlight sword in Armored Core 6 - Polygon10 abril 2025
How to get the Moonlight sword in Armored Core 6 - Polygon10 abril 2025 -
 Technoblade Never Dies 1999-2022 Unisex T-Shirt - REVER LAVIE10 abril 2025
Technoblade Never Dies 1999-2022 Unisex T-Shirt - REVER LAVIE10 abril 2025 -
 Rabiscos & Cenas: Troca equivalente – Anime FullMetal Alchemist10 abril 2025
Rabiscos & Cenas: Troca equivalente – Anime FullMetal Alchemist10 abril 2025 -
 Let's Play Pokémon Infinite Fusion Part 9: Old Men and Sailors and Krab's Legs OH MY – Curated Critiques10 abril 2025
Let's Play Pokémon Infinite Fusion Part 9: Old Men and Sailors and Krab's Legs OH MY – Curated Critiques10 abril 2025 -
 Fantasia De Halloween Infantil Festa Vampiro Baby Menino10 abril 2025
Fantasia De Halloween Infantil Festa Vampiro Baby Menino10 abril 2025 -
Camiseta Camisas Moto Robozão Rua Grau 244 Não É Crime10 abril 2025
-
 CR7 amazing elastico nutmeg today (Y) : r/gifs10 abril 2025
CR7 amazing elastico nutmeg today (Y) : r/gifs10 abril 2025 -
/media/articles/main/2019/03/02/7bc3754b-cae2-4398-9e77-8cc59643efc2-3407374419.jpg) Kengan Ashura - Anime ganha dois novos vídeos!, Notícias10 abril 2025
Kengan Ashura - Anime ganha dois novos vídeos!, Notícias10 abril 2025 -
Kuma Kuma Kuma Bear10 abril 2025
-
 Buy Roblox Gift Card USD/EUR, Roblox Code in BD10 abril 2025
Buy Roblox Gift Card USD/EUR, Roblox Code in BD10 abril 2025

