Extra high superoxide dismutase in host tissue is associated with
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 03 abril 2025
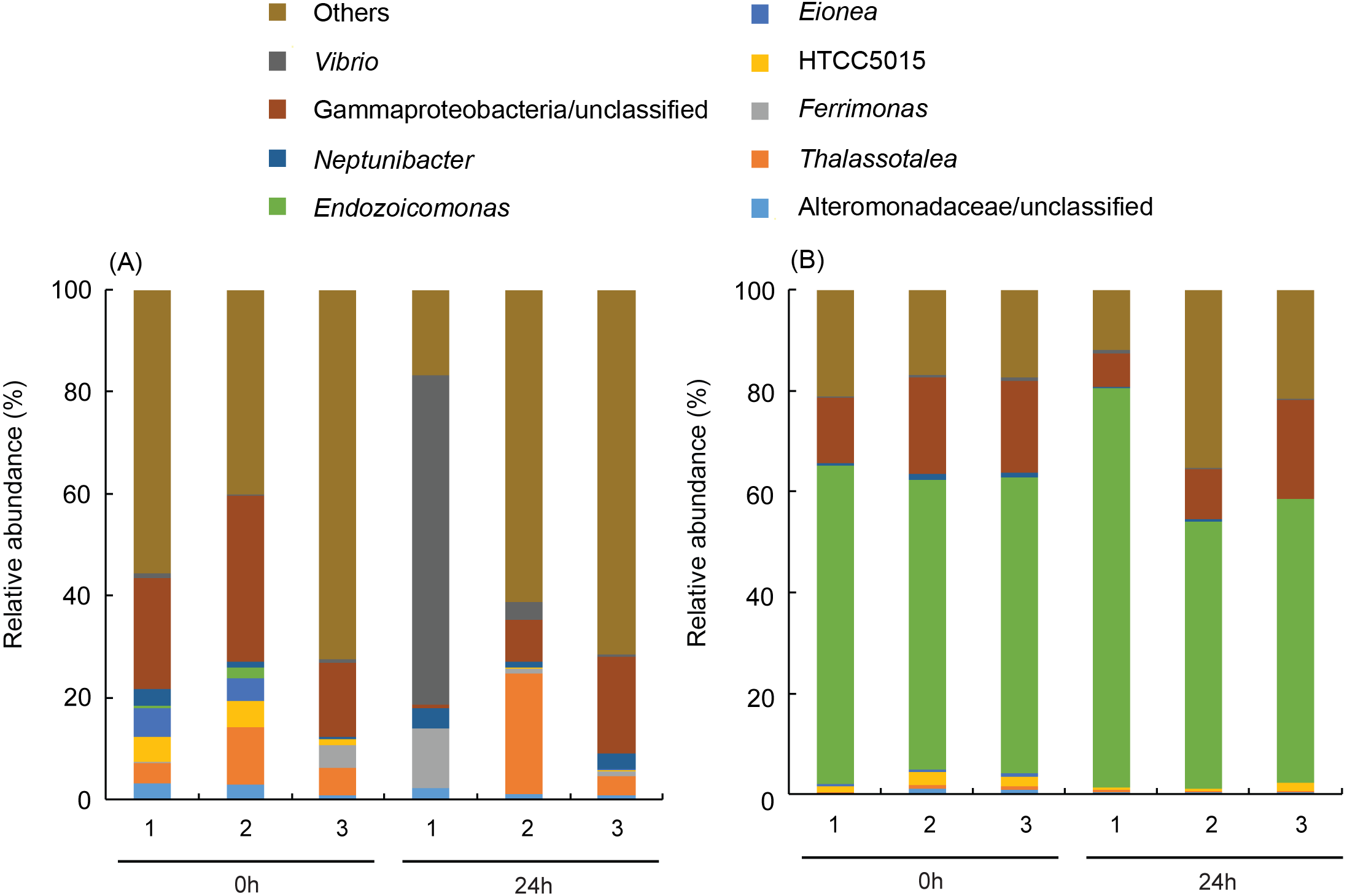
Global warming threatens reef-building corals with large-scale bleaching events; therefore, it is important to discover potential adaptive capabilities for increasing their temperature resistance before it is too late. This study presents two coral species (Platygyra verweyi and Isopora palifera) surviving on a reef having regular hot water influxes via a nearby nuclear power plant that exhibited completely different bleaching susceptibilities to thermal stress, even though both species shared several so-called “winner” characteristics (e.g., containing Durusdinium trenchii, thick tissue, etc.). During acute heating treatment, algal density did not decline in P. verweyi corals within three days of being directly transferred from 25 to 31 °C; however, the same treatment caused I. palifera to lose < 70% of its algal symbionts within 24 h. The most distinctive feature between the two coral species was an overwhelmingly higher constitutive superoxide dismutase (ca. 10-fold) and catalase (ca. 3-fold) in P. verweyi over I. palifera. Moreover, P. verweyi also contained significantly higher saturated and lower mono-unsaturated fatty acids, especially a long-chain saturated fatty acid (C22:0), than I. palifera, and was consistently associated with the symbiotic bacteria Endozoicomonas, which was not found in I. palifera. However, antibiotic treatment and inoculation tests did not support Endozoicomonas having a direct contribution to thermal resistance. This study highlights that, besides its association with a thermally tolerable algal symbiont, a high level of constitutive antioxidant enzymes in the coral host is crucial for coral survivorship in the more fluctuating and higher temperature environments.
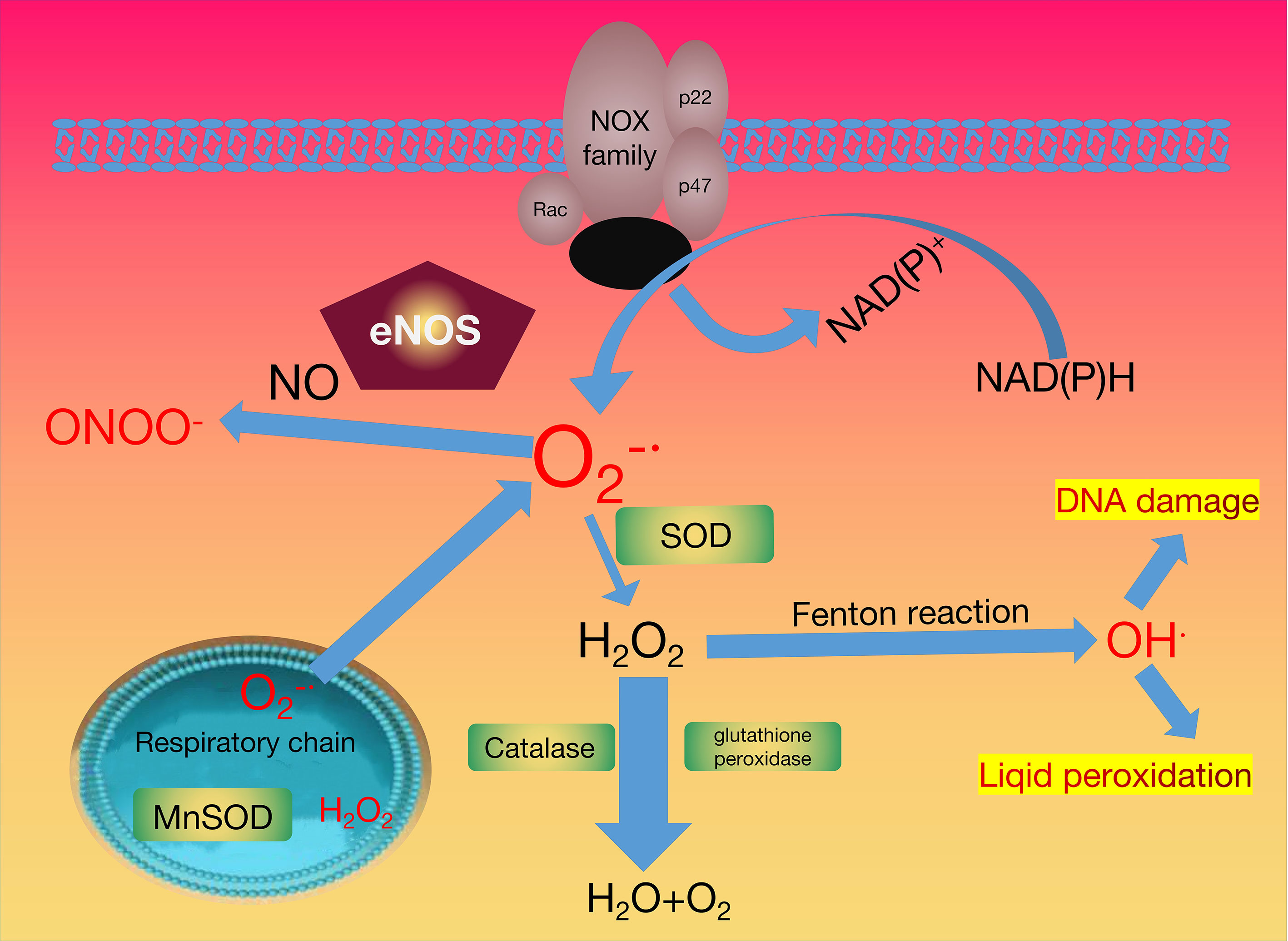
Frontiers Emerging Antioxidant Paradigm of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Therapy
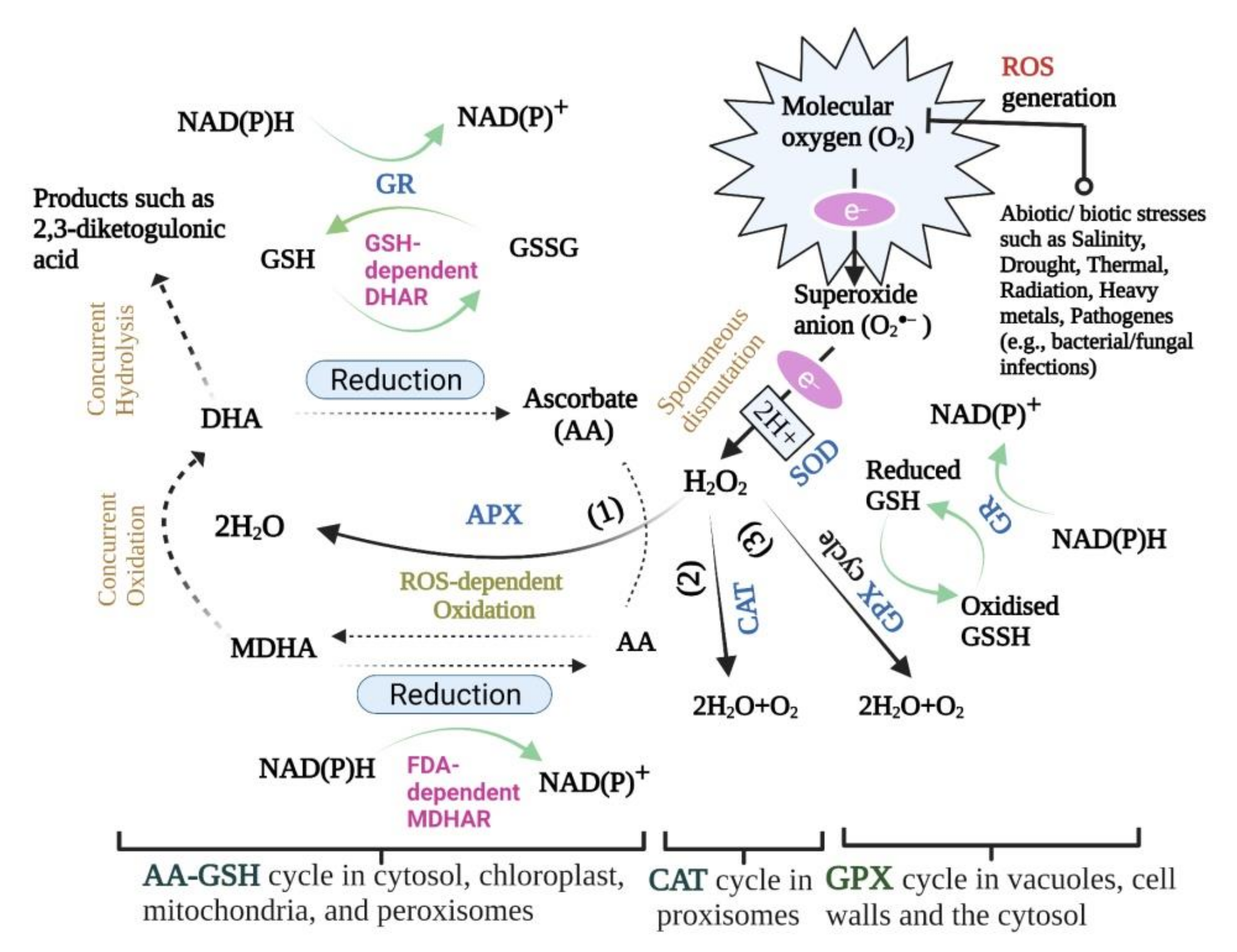
Biology, Free Full-Text

Hint from an Enzymatic Reaction: Superoxide Dismutase Models Efficiently Suppress Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation

PDF) Superoxide Dismutase: A Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
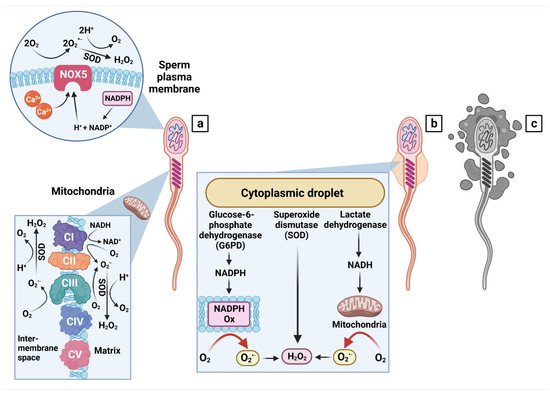
Oxygen, Free Full-Text
Identification and Molecular Characterization of Superoxide Dismutases Isolated From A Scuticociliate Parasite: Physiological Role in Oxidative Stress
Pharmaceuticals, Free Full-Text
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

Human CD4+CD25+ T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor against aberrant superoxide dismutase 1 trigger antigen-specific immunomodulation - Cytotherapy

Endogenous SOD2 (Superoxide Dismutase) Regulates Platelet-Dependent Thrombin Generation and Thrombosis During Aging
Frontiers Signaling pathways of oxidative stress response: the potential therapeutic targets in gastric cancer

Isoliquiritigenin attenuates high-fat diet-induced intestinal damage by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress and through activating Nrf2 - ScienceDirect

a) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity (USOD/ mg protein) (b)
Recomendado para você
-
Edileuza Silveira - Analista societário - TIME CONTROL03 abril 2025
-
 Successful Premiere at Control Trade Show for QATM03 abril 2025
Successful Premiere at Control Trade Show for QATM03 abril 2025 -
 Boomer's Rise (RUTHLESS KINGS MC™ ATLANTIC CITY)03 abril 2025
Boomer's Rise (RUTHLESS KINGS MC™ ATLANTIC CITY)03 abril 2025 -
 Original photoMike Tyson and Don King Las Vagas03 abril 2025
Original photoMike Tyson and Don King Las Vagas03 abril 2025 -
 Proprli Vagas abertas em Tecnologia03 abril 2025
Proprli Vagas abertas em Tecnologia03 abril 2025 -
 Healthy Gut, Healthy You03 abril 2025
Healthy Gut, Healthy You03 abril 2025 -
 Your vegus nerve and constipation - 7 ways to help03 abril 2025
Your vegus nerve and constipation - 7 ways to help03 abril 2025 -
 Accessibility at events: 6 tips for your planning - Hand Talk03 abril 2025
Accessibility at events: 6 tips for your planning - Hand Talk03 abril 2025 -
 The Limits of Control: Lines of Power in Todd Field's Tár on03 abril 2025
The Limits of Control: Lines of Power in Todd Field's Tár on03 abril 2025 -
 AI Accessibility: what are AI assistive technology examples?03 abril 2025
AI Accessibility: what are AI assistive technology examples?03 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Forever 21 In Times Square by emptyyeyes on DeviantArt03 abril 2025
Forever 21 In Times Square by emptyyeyes on DeviantArt03 abril 2025 -
my hero academia chapter 402 all might|TikTok Search03 abril 2025
-
 Pokemon Eevee Evolution Premium Collection 6-Box Case03 abril 2025
Pokemon Eevee Evolution Premium Collection 6-Box Case03 abril 2025 -
 Isca Artificial Nelson Nakamura Nakamarão 7cm Camarão - Cartela03 abril 2025
Isca Artificial Nelson Nakamura Nakamarão 7cm Camarão - Cartela03 abril 2025 -
 PLAYSTATION: PS4 com dois controles, dois jogos é funci03 abril 2025
PLAYSTATION: PS4 com dois controles, dois jogos é funci03 abril 2025 -
 1.3inch Color Screen Smart Bracelet Waterproof Sport Smart Watch Heart Rate Blood Pressure Sleep Fitness Wristband Pedometer Call SMS Sedenetary Reminder Activity Tracker Smartband For IOS Android - buy 1.3inch Color Screen03 abril 2025
1.3inch Color Screen Smart Bracelet Waterproof Sport Smart Watch Heart Rate Blood Pressure Sleep Fitness Wristband Pedometer Call SMS Sedenetary Reminder Activity Tracker Smartband For IOS Android - buy 1.3inch Color Screen03 abril 2025 -
 KNOWER, Twitter, Instagram, Facebook03 abril 2025
KNOWER, Twitter, Instagram, Facebook03 abril 2025 -
 Revelando os mistérios da anisotropia - Glastory03 abril 2025
Revelando os mistérios da anisotropia - Glastory03 abril 2025 -
 SHOWCASE DA SENGOKU E TA MUITO FORTE NO SHINDO LIFE03 abril 2025
SHOWCASE DA SENGOKU E TA MUITO FORTE NO SHINDO LIFE03 abril 2025 -
 Imagens Bola Amarela PNG e Vetor, com Fundo Transparente Para03 abril 2025
Imagens Bola Amarela PNG e Vetor, com Fundo Transparente Para03 abril 2025

