Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 28 março 2025
The genus Aspergillus, one of the most abundant airborne fungi, is classified into hundreds of species that affect humans, animals, and plants. Among these, Aspergillus nidulans, as a key model organism, has been extensively studied to understand the mechanisms governing growth and development, physiology, and gene regulation in fungi. A. nidulans primarily reproduces by forming millions of asexual spores known as conidia. The asexual life cycle of A. nidulans can be simply divided into growth and asexual development (conidiation). After a certain period of vegetative growth, some vegetative cells (hyphae) develop into specialized asexual structures called conidiophores. Each A. nidulans conidiophore is composed of a foot cell, stalk, vesicle, metulae, phialides, and 12,000 conidia. This vegetative-to-developmental transition requires the activity of various regulators including FLB proteins, BrlA, and AbaA. Asymmetric repetitive mitotic cell division of phialides results in the formation of immature conidia. Subsequent conidial maturation requires multiple regulators such as WetA, VosA, and VelB. Matured conidia maintain cellular integrity and long-term viability against various stresses and desiccation. Under appropriate conditions, the resting conidia germinate and form new colonies, and this process is governed by a myriad of regulators, such as CreA and SocA. To date, a plethora of regulators for each asexual developmental stage have been identified and investigated. This review summarizes our current understanding of the regulators of conidial formation, maturation, dormancy, and germination in A. nidulans.
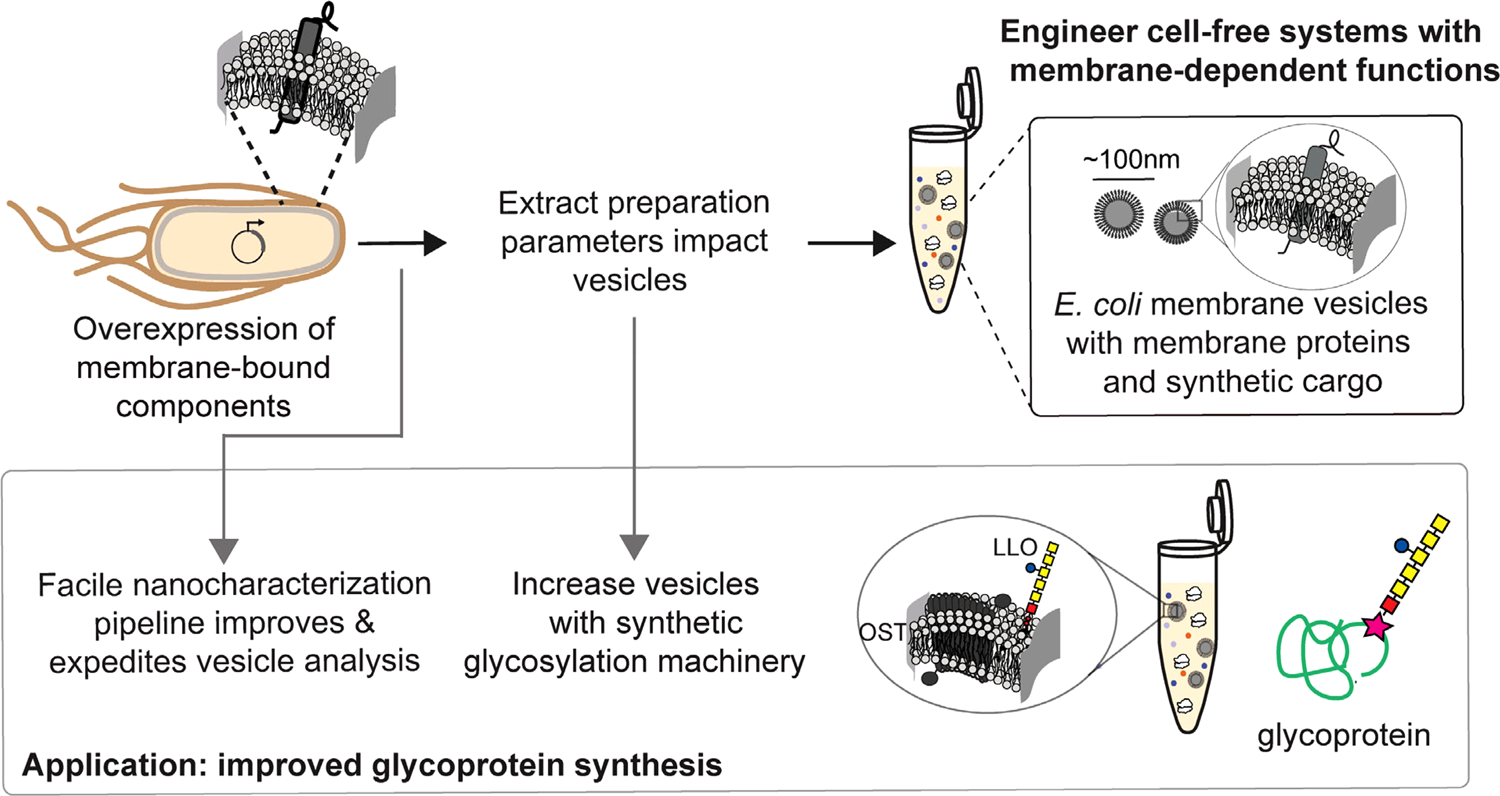
Improving cell-free glycoprotein synthesis by characterizing and enriching native membrane vesicles
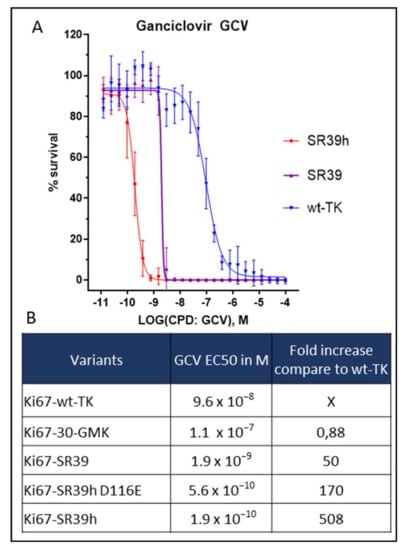
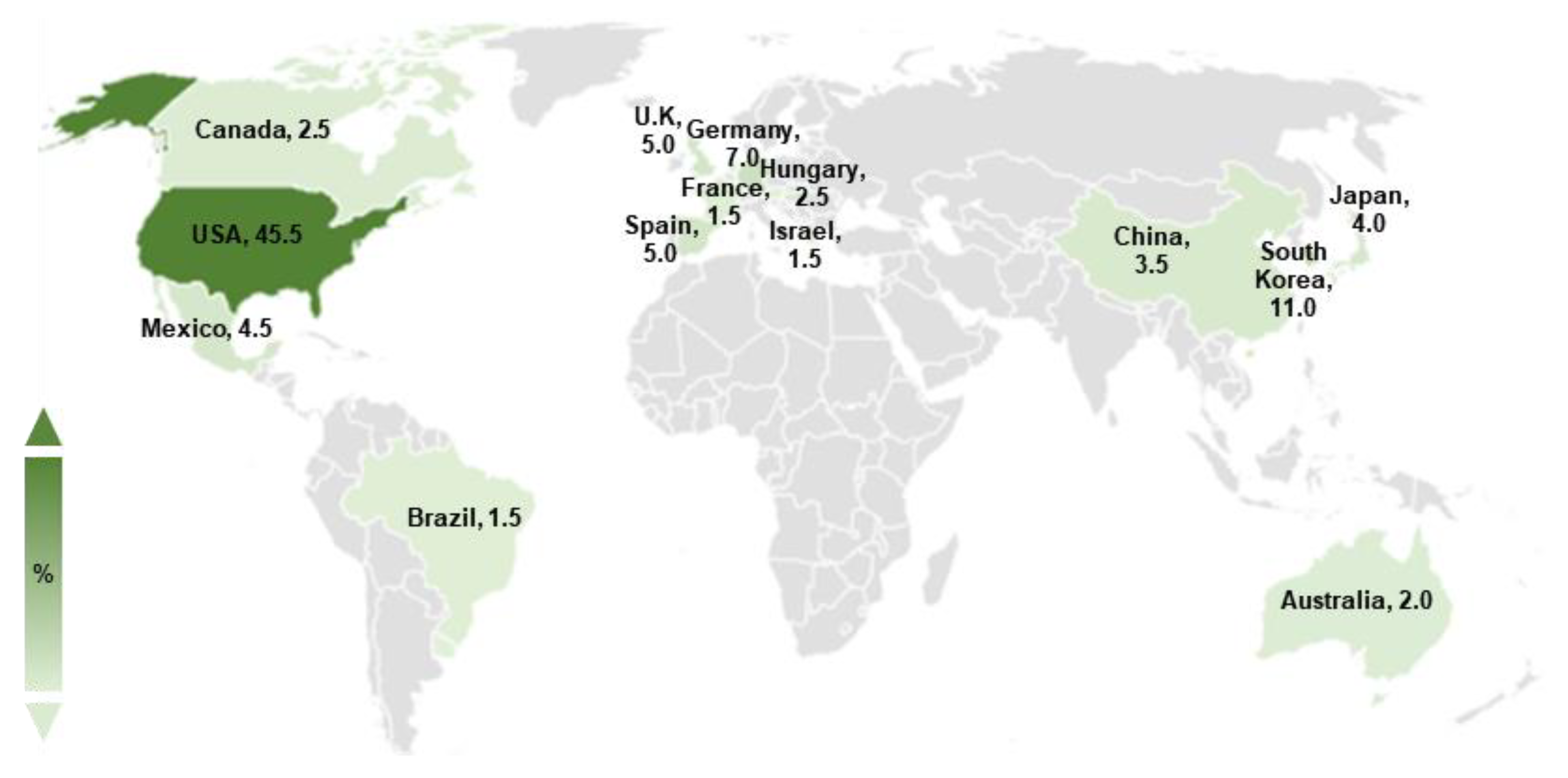
Serial Number Alcohol 120 1.9 6 - Colaboratory

The emerging impact of cell-free chemical biosynthesis - ScienceDirect
PDF) Protein structural biology using cell-free platform from wheat germ

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy
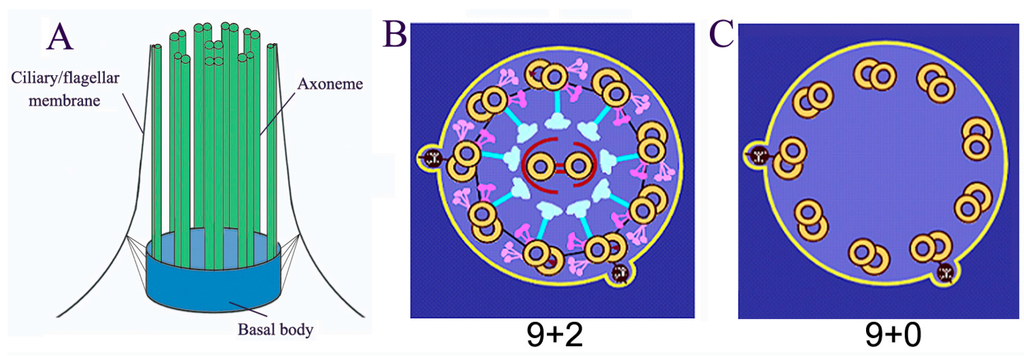
Cells, Free Full-Text
THE CELL : PAUL REVERE11 : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
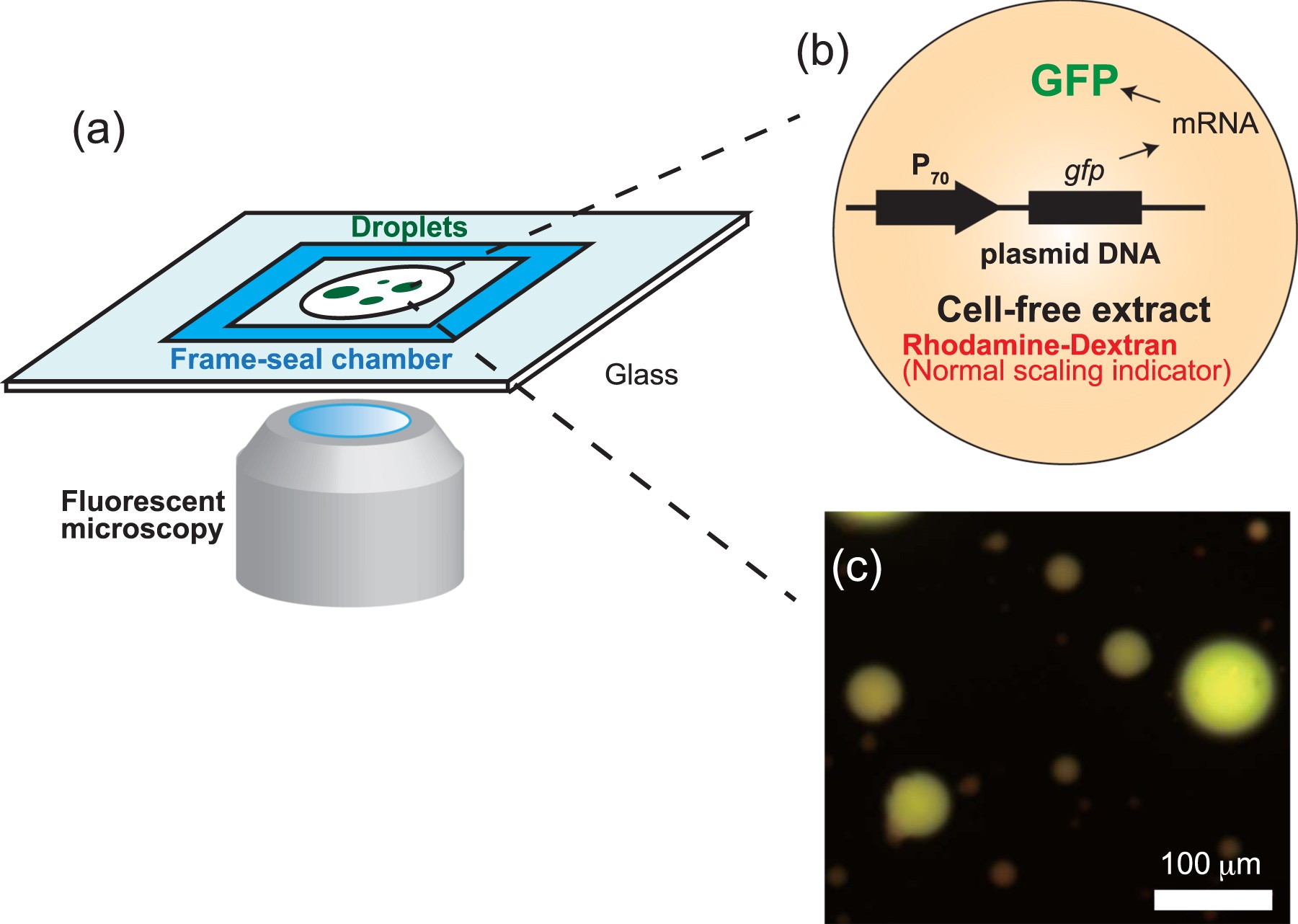
Anomalous Scaling of Gene Expression in Confined Cell-Free Reactions

Rapid cell-free characterization of multi-subunit CRISPR effectors and transposons - ScienceDirect

Cell-free synthetic biology: Engineering in an open world - ScienceDirect

Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Methods and Protocols

Cells, Free Full-Text
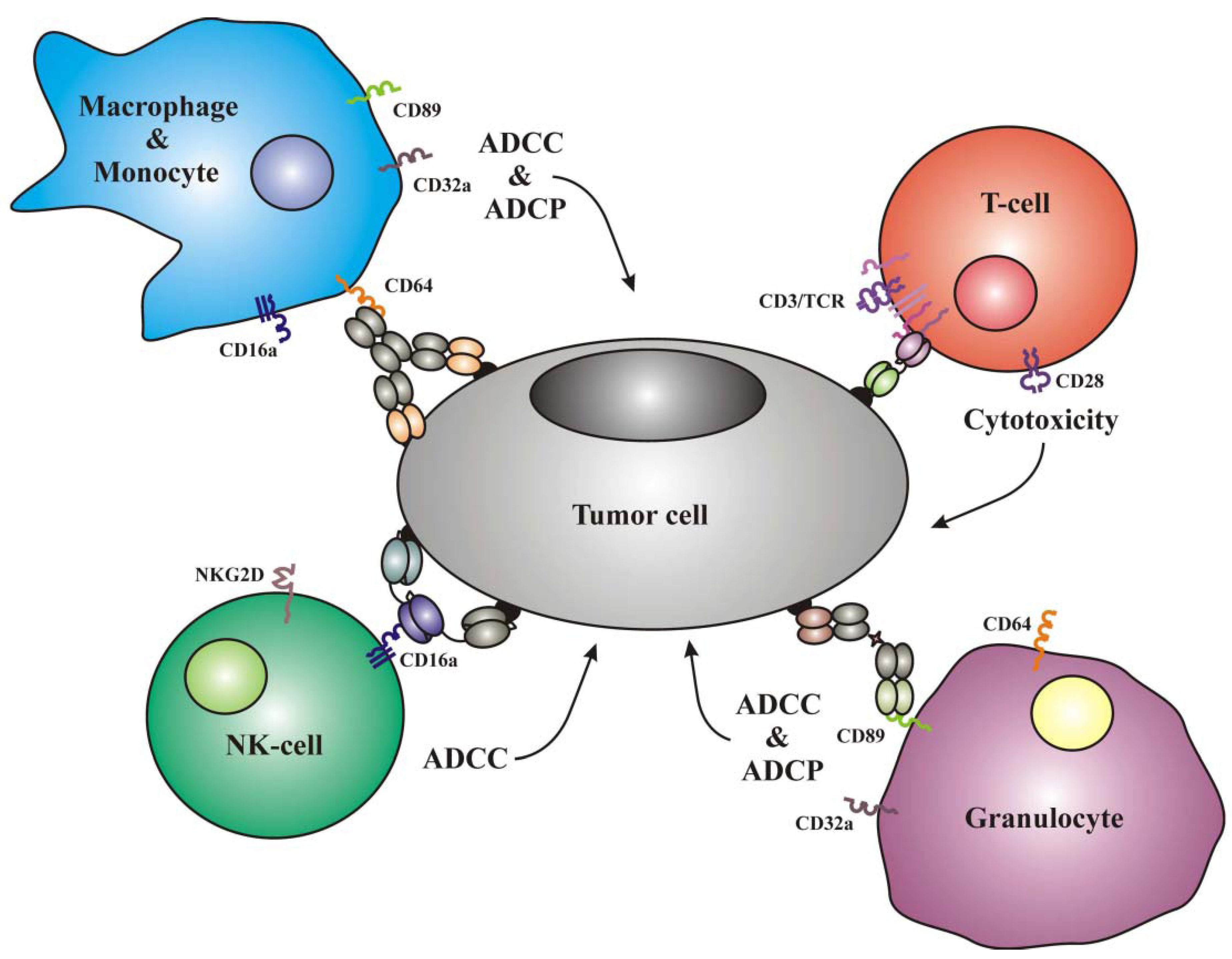
Antibodies, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 One Piece Todos arcos que a 1ª temporada da série da Netflix adapta28 março 2025
One Piece Todos arcos que a 1ª temporada da série da Netflix adapta28 março 2025 -
 One piece28 março 2025
One piece28 março 2025 -
 One Piece's Luffy among new Thanksgiving Parade balloons, Lifestyle28 março 2025
One Piece's Luffy among new Thanksgiving Parade balloons, Lifestyle28 março 2025 -
 Luffy Minecraft Skins28 março 2025
Luffy Minecraft Skins28 março 2025 -
luffy scale força|Pesquisa do TikTok28 março 2025
-
 Como você seria em One Piece28 março 2025
Como você seria em One Piece28 março 2025 -
 Quanto vc conhece o jimimdabucisuja28 março 2025
Quanto vc conhece o jimimdabucisuja28 março 2025 -
 piczeto de jose :v (calvo) by CucoRRR on DeviantArt28 março 2025
piczeto de jose :v (calvo) by CucoRRR on DeviantArt28 março 2025 -
 2 TURN EVENT BOSS DEMONIC BEAST GLOOM - Grand Cross28 março 2025
2 TURN EVENT BOSS DEMONIC BEAST GLOOM - Grand Cross28 março 2025 -
Falando Sobre Animes .28 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
Top Tier FCU - Apps on Google Play28 março 2025
-
 Watch Valvrave the Liberator season 1 episode 7 streaming online28 março 2025
Watch Valvrave the Liberator season 1 episode 7 streaming online28 março 2025 -
 Gallery Turned Ninja – Tagged Dragon Ball Super28 março 2025
Gallery Turned Ninja – Tagged Dragon Ball Super28 março 2025 -
 Fã de Dragon Ball fez uma arte épica do Super Saiyajin 5 - Critical Hits28 março 2025
Fã de Dragon Ball fez uma arte épica do Super Saiyajin 5 - Critical Hits28 março 2025 -
 Cross Road Blues (Crossroads)" Sheet Music by Eric Clapton; Cream for Guitar Tab - Sheet Music Now28 março 2025
Cross Road Blues (Crossroads)" Sheet Music by Eric Clapton; Cream for Guitar Tab - Sheet Music Now28 março 2025 -
 First Minecraft MOBA Server, League of Legends Server, Now public after two years!28 março 2025
First Minecraft MOBA Server, League of Legends Server, Now public after two years!28 março 2025 -
 Here's a thing — snazzamazing: made some more icons requested by28 março 2025
Here's a thing — snazzamazing: made some more icons requested by28 março 2025 -
 Kaguya-sama wa Kokurasetai: Tensai-tachi no Renai Zunousen – 05 - Lost in Anime28 março 2025
Kaguya-sama wa Kokurasetai: Tensai-tachi no Renai Zunousen – 05 - Lost in Anime28 março 2025 -
 Stranger Things (4.ª temporada) – Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre28 março 2025
Stranger Things (4.ª temporada) – Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre28 março 2025 -
 What is The Max Level Cap in God of War Ragnarok? Answered28 março 2025
What is The Max Level Cap in God of War Ragnarok? Answered28 março 2025

