Bacon's Rebellion, Part 2
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 01 abril 2025
Historian Robert Dunkerly talked about the effects of Nathaniel Bacon
Historian Robert Dunkerly talked about the effects of Nathaniel Bacon’s violent uprising against the British Colonial Governor in Virginia. In the second part of this two-part class, he spoke about the decline of the rebellion, the aftermath, and how the event is remembered by historians.
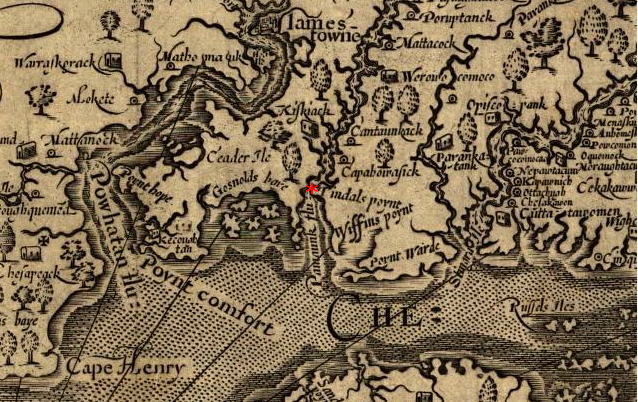
In 1676, Nathaniel Bacon led a group of armed settlers against the Colonial Government of Virginia, claiming that Governor William Berkeley was corrupt and had unfairly taxed the colonists. The rebels also asserted that leaders had failed to defend Virginians from Native American attacks. Bacon’s Rebellion attacked Native American villages, killing men, women, and children, then later sacked and burned the capital of Jamestown to the ground. After Bacon died of dysentery, the rebellion collapsed and was quelled by forces loyal to the Governor.
Historian Robert Dunkerly talked about the effects of Nathaniel Bacon’s violent uprising against the British Colonial Governor in Virginia. In the second part of this two-part class, he spoke about the decline of the rebellion, the aftermath, and how the event is remembered by historians.
In 1676, Nathaniel Bacon led a group of armed settlers against the Colonial Government of Virginia, claiming that Governor William Berkeley was corrupt and had unfairly taxed the colonists. The rebels also asserted that leaders had failed to defend Virginians from Native American attacks. Bacon’s Rebellion attacked Native American villages, killing men, women, and children, then later sacked and burned the capital of Jamestown to the ground. After Bacon died of dysentery, the rebellion collapsed and was quelled by forces loyal to the Governor.

Bacon's Rebellion, 1676 by Wertenbaker, Thomas Jefferson

King Philip's War and Bacon's Rebellion: Colonial Paradigms and
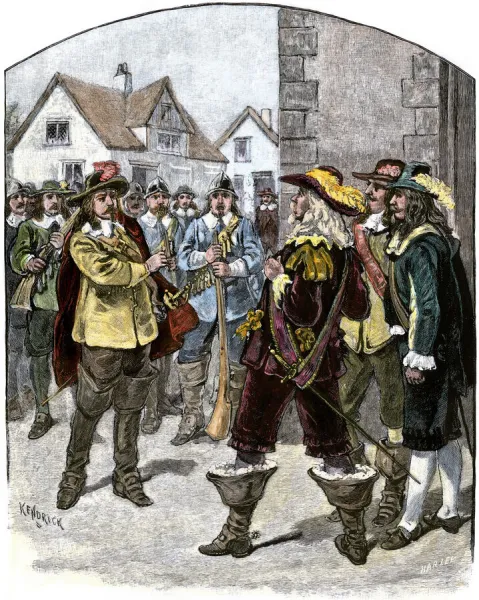

Bacons Rebellion in Jamestown, 1676 available as Framed Prints

Bacon's Rebellion New Visions - Social Studies
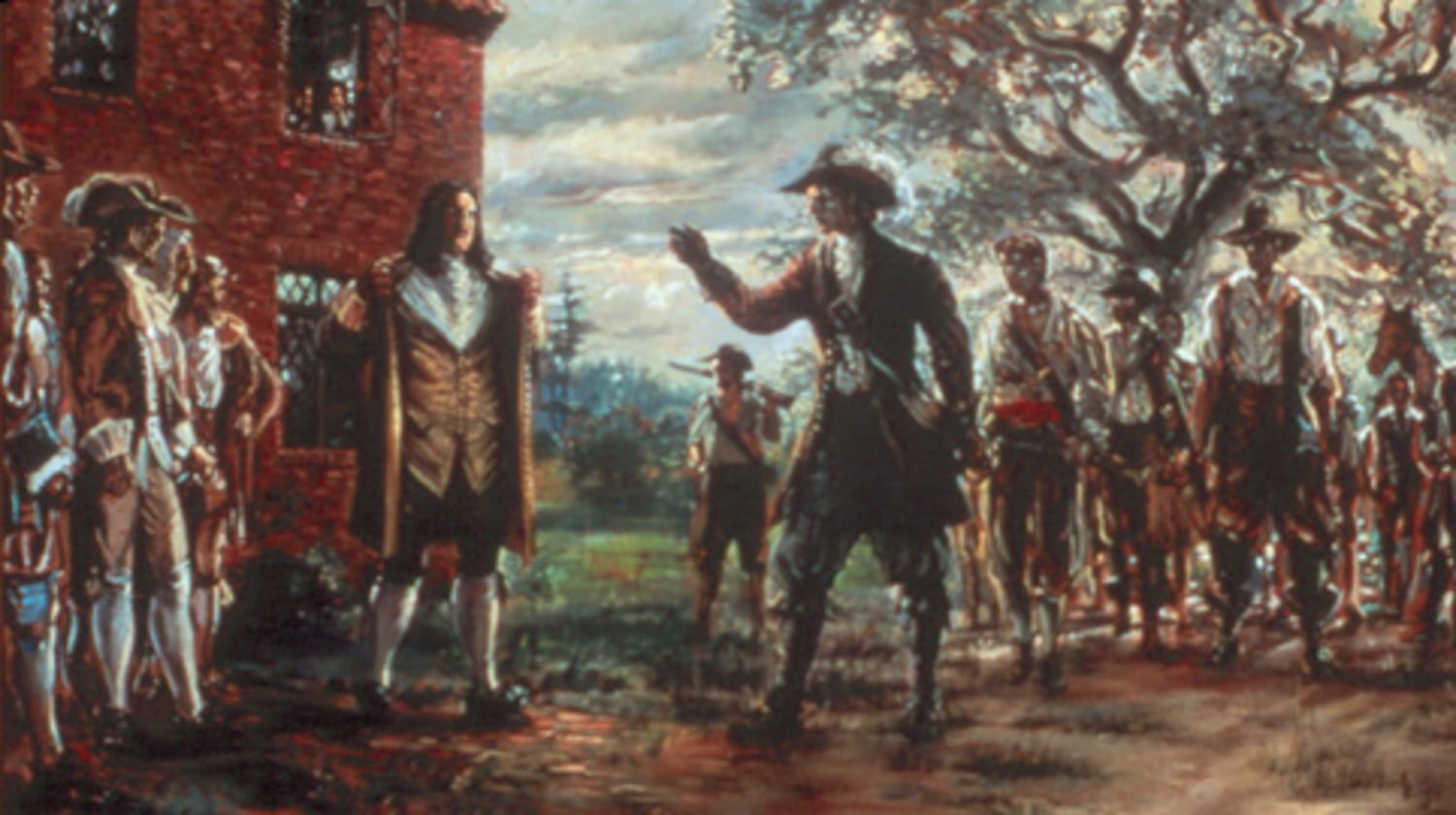

1600-1770: The colonial experience

Bacon's Rebellion (1676–1677) - Encyclopedia Virginia

Prelude to Bacon's Rebelion in 1676

Exact Definition of Rebellion - Bacon's Rebellion

Bacon's Rebellion Significance, Causes & Effects - Video

The Reacting Consortium - Bacon's Rebellion

Frontier Politics, Providentialism, and “Hobbism” in Bacon's
Recomendado para você
-
 Bacon's Rebellion (1676–1677) - Encyclopedia Virginia01 abril 2025
Bacon's Rebellion (1676–1677) - Encyclopedia Virginia01 abril 2025 -
 Bacon's Rebellion - World History Encyclopedia01 abril 2025
Bacon's Rebellion - World History Encyclopedia01 abril 2025 -
Bacon's Rebellion: America's First Armed Insurrection01 abril 2025
-
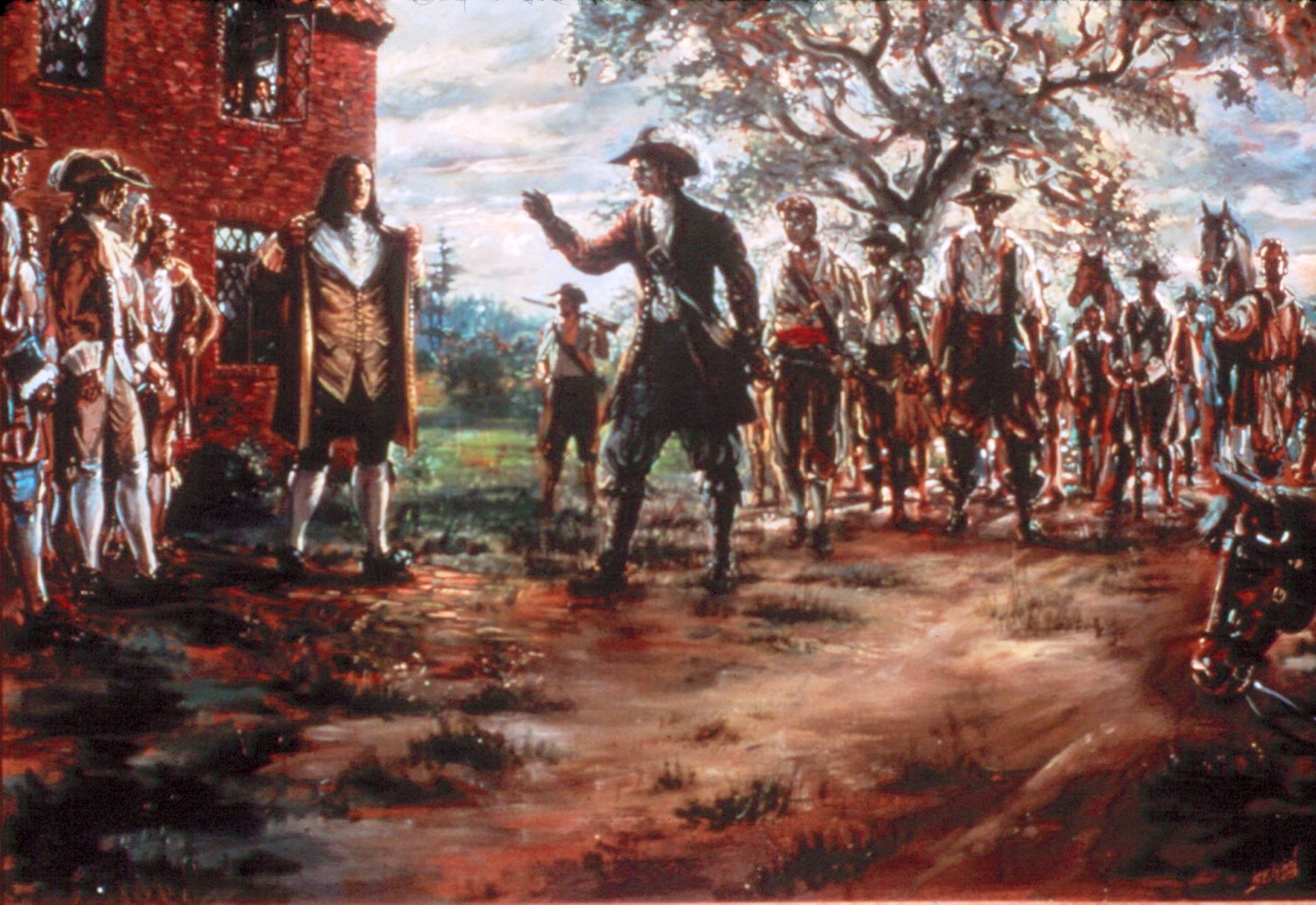 Bacon's Rebellion in 167601 abril 2025
Bacon's Rebellion in 167601 abril 2025 -
 Bacon's Rebellion Facts & Summary Lesson for Kids - Video & Lesson01 abril 2025
Bacon's Rebellion Facts & Summary Lesson for Kids - Video & Lesson01 abril 2025 -
 Tales from a Revolution: Bacon's Rebellion by Rice, James D.01 abril 2025
Tales from a Revolution: Bacon's Rebellion by Rice, James D.01 abril 2025 -
 Biography of Nathaniel Bacon - Bacon's Rebellion01 abril 2025
Biography of Nathaniel Bacon - Bacon's Rebellion01 abril 2025 -
 Bacon's Rebellion Lesson/Stations by Hey Ms Vee01 abril 2025
Bacon's Rebellion Lesson/Stations by Hey Ms Vee01 abril 2025 -
 Bacon's Rebellion (or, “Why is Bacon so Angry?). - ppt download01 abril 2025
Bacon's Rebellion (or, “Why is Bacon so Angry?). - ppt download01 abril 2025 -
 Bacon's Rebellion – Thorowgood World01 abril 2025
Bacon's Rebellion – Thorowgood World01 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 ¡DESBLOQUEA OBJETOS EN LOS SIMS 4 CON ESTOS TRUCOS01 abril 2025
¡DESBLOQUEA OBJETOS EN LOS SIMS 4 CON ESTOS TRUCOS01 abril 2025 -
 70 anos da FIERJ – Teresa Bergher – vereadora do Rio de Janeiro01 abril 2025
70 anos da FIERJ – Teresa Bergher – vereadora do Rio de Janeiro01 abril 2025 -
 Resident Evil Dr Livesey walking meme01 abril 2025
Resident Evil Dr Livesey walking meme01 abril 2025 -
 This PERFECT WARM-UP WILL DOUBLE YOUR AIM on EVERY HERO - BEST01 abril 2025
This PERFECT WARM-UP WILL DOUBLE YOUR AIM on EVERY HERO - BEST01 abril 2025 -
 Death Stranding Metacritic Scores - How Is Kojima's Latest Faring01 abril 2025
Death Stranding Metacritic Scores - How Is Kojima's Latest Faring01 abril 2025 -
 ran away from existence?, weirdcore/dreamcore01 abril 2025
ran away from existence?, weirdcore/dreamcore01 abril 2025 -
 6pcs Happy Family Barbie Midge Pregnant Newborn Baby Girl Doll 1.75”01 abril 2025
6pcs Happy Family Barbie Midge Pregnant Newborn Baby Girl Doll 1.75”01 abril 2025 -
 Free to play, ¿Qué significa Free to play?01 abril 2025
Free to play, ¿Qué significa Free to play?01 abril 2025 -
PS4 2022 Games - Def Jam Fight for NY PS201 abril 2025
-
 Jogo de 4 copos de aperitivo em vidro com dizeres.01 abril 2025
Jogo de 4 copos de aperitivo em vidro com dizeres.01 abril 2025

