A comparison of Esmolol and Labetalol for Attenuation of Sympathomimetic Responses to Laryngoscopy and Intubation
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 27 abril 2025

Both Labetalol and Esmolol in low doses are not effective in attenuation of sympathomimetic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation. ABSTRACT: Objective: The study was designed to Compare esmolol and labetolol for attenuation of sympathomimetic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation. Materials & Methods: 80 patients were randomly divided into two groups by prospective randomized single blind study, 40 patients received labetolol 0.5mg/kg and other patients received esmolol 0.25mg/kg. The baseline heart rate, BP, Spo2 were recorded & Compared. Conclusion: both Labetalol ( 0.25mg/kg ) and Esmolol (0.5 mg/kg ) in low doses are not effective in attenuation of sympathomimetic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation .

PDF) Attenuation of hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation -comparison of fentanyl, esmolol and metoprolol in normotensive individuals
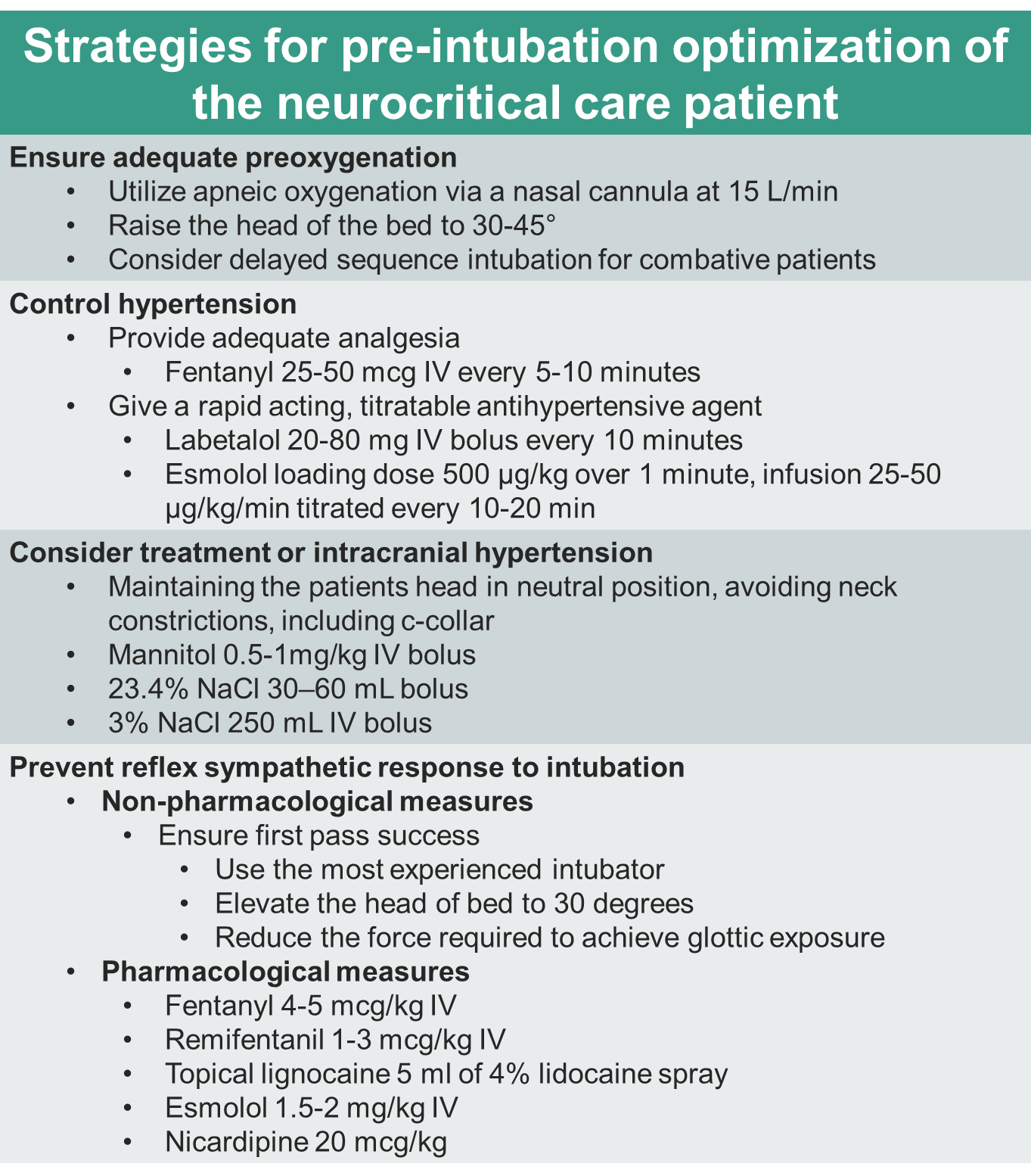
AAEM Resident and Student Association : Pre-intubation Optimization of the Neurocritical Care Patient

PDF) Attenuation of hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation -comparison of fentanyl, esmolol and metoprolol in normotensive individuals

PDF) Attenuation of hypertensive response with esmolol and labetalol in low doses in orotracheal intubation: A comparative study
PDF) Comparison of esmolol and labetalol, in low doses, for attenuation of sympathomimetic response to laryngoscopy and intubation

To evaluate the efficacy between 0.15mg/Kg and 0.25mg/Kg of iv labetalol in the suppression of haemodynamic response to extubation - IJCA

Dexmedetomidine for Attenuation of Sympathomimetic Response to Laryngoscopy and Tracheal Intubation in Neurosurgical Patients Sen B, Sen J - J Datta Meghe Inst Med Sci Univ
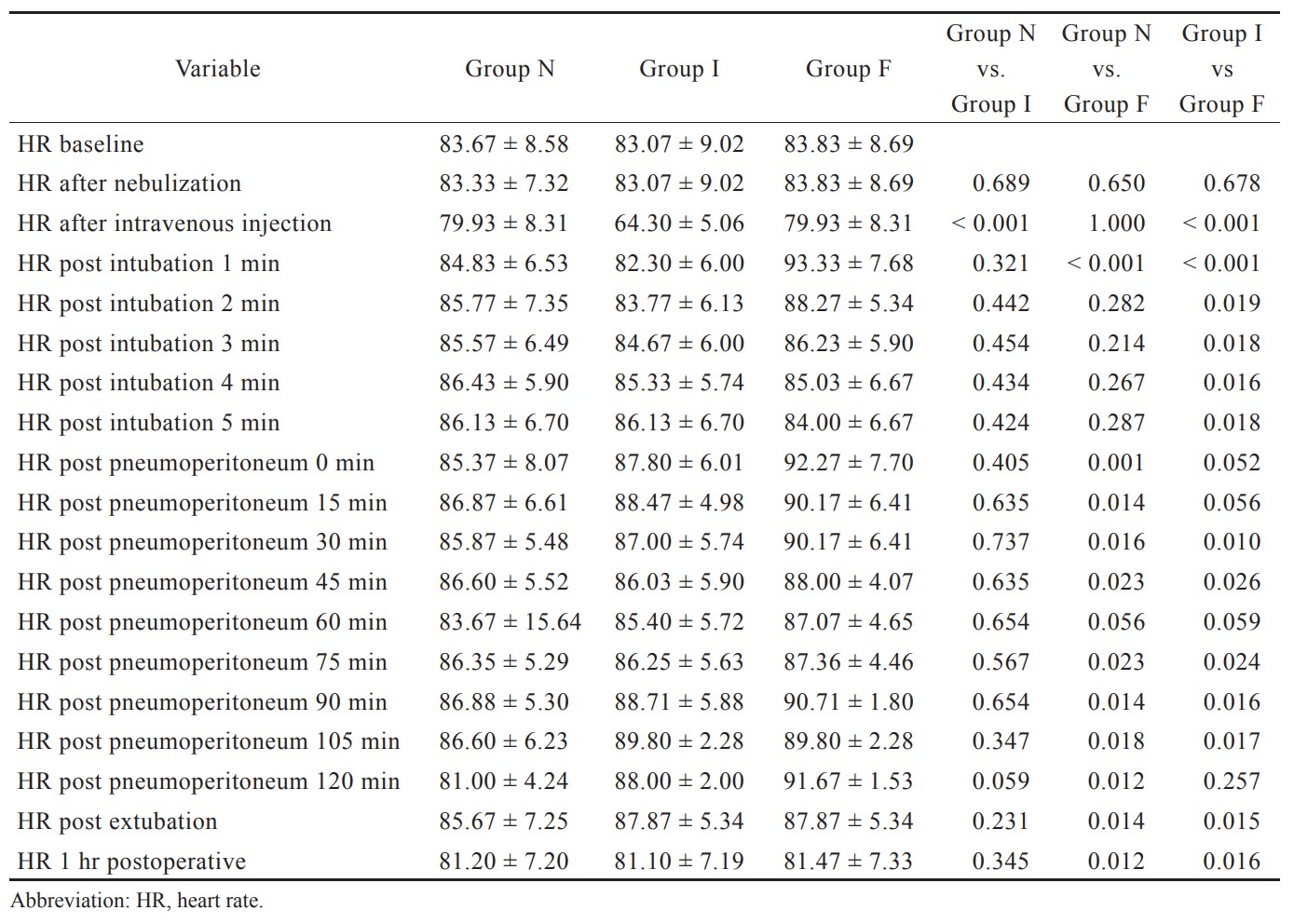
Comparison of Hemodynamics and Opioid Sparing Effect of Dexmedetomidine Nebulization and Intravenous Dexmedetomidine in Laparoscopic Surgeries Under General Anesthesia

Intravenous Amiodarone and Sotalol Impair Contractility and Cardiac Output, but Procainamide Does Not: A Langendorff Study - Charles Mackin, Elizabeth S. DeWitt, Katherine J. Black, Xiaoqi Tang, Brian D. Polizzotti, Sarah J.
Recomendado para você
-
Labetalol Hydrochloride Injection27 abril 2025
-
Labetalol (Normodyne) Vial, 5mg/mL27 abril 2025
-
 Labetalol Hydrochloride Injection USP 100mg/20ml27 abril 2025
Labetalol Hydrochloride Injection USP 100mg/20ml27 abril 2025 -
 Labetalol LABETALOL, Labetalol HCL Inj; Vial; 5mg/mL. 20 mL $28.75/Each17478-0420-2027 abril 2025
Labetalol LABETALOL, Labetalol HCL Inj; Vial; 5mg/mL. 20 mL $28.75/Each17478-0420-2027 abril 2025 -
 LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated27 abril 2025
LABETALOL HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated27 abril 2025 -
 Labetalol Tablets: Package Insert27 abril 2025
Labetalol Tablets: Package Insert27 abril 2025 -
 LABETALOL INJ 5MG/ML - RX Products27 abril 2025
LABETALOL INJ 5MG/ML - RX Products27 abril 2025 -
 Labetalol Injection, 5 Ml, Prescription27 abril 2025
Labetalol Injection, 5 Ml, Prescription27 abril 2025 -
 BUY Labetalol Hydrochloride (Labetalol Hydrochloride) 5 mg/mL from GNH India at the best price available.27 abril 2025
BUY Labetalol Hydrochloride (Labetalol Hydrochloride) 5 mg/mL from GNH India at the best price available.27 abril 2025 -
 Hypertension Third leading cause of maternal mortality, after thromboembolism and non-obstetric injuries Maternal DBP > 110 is associated with ↑ risk of. - ppt download27 abril 2025
Hypertension Third leading cause of maternal mortality, after thromboembolism and non-obstetric injuries Maternal DBP > 110 is associated with ↑ risk of. - ppt download27 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Teoria dos jogos – Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre27 abril 2025
Teoria dos jogos – Wikipédia, a enciclopédia livre27 abril 2025 -
 Morre Cláudio Satiro, dublador de 50 Cent em 'Sangue no Gelo27 abril 2025
Morre Cláudio Satiro, dublador de 50 Cent em 'Sangue no Gelo27 abril 2025 -
Assista Shingeki no Kyojin (Attack On Titan) Dublado e Legendado27 abril 2025
-
 Pokémon TCG Shaymin V Full Art Brilliant Stars 152/172 NM+ Non Played27 abril 2025
Pokémon TCG Shaymin V Full Art Brilliant Stars 152/172 NM+ Non Played27 abril 2025 -
 Atacante flagrado no doping na final da Libertadores é suspenso27 abril 2025
Atacante flagrado no doping na final da Libertadores é suspenso27 abril 2025 -
 Will Squid Game: The Challenge be the darkest reality show ever?, Squid Game27 abril 2025
Will Squid Game: The Challenge be the darkest reality show ever?, Squid Game27 abril 2025 -
 THIS ROBLOX GAME IS SUS 😳27 abril 2025
THIS ROBLOX GAME IS SUS 😳27 abril 2025 -
 finally snake cheto free ho gaya 😱 link in description watch full video27 abril 2025
finally snake cheto free ho gaya 😱 link in description watch full video27 abril 2025 -
 Cities Skylines 2 first performance patch hits Steam but not Game27 abril 2025
Cities Skylines 2 first performance patch hits Steam but not Game27 abril 2025 -
Jogos das 3 pistas, Program Silvio Santos (02/05/19), No jogo das 3 pistas deste domingo teve Izabella Camargo x Fernando Rocha, vem conferir! 😍👏, By Programa Silvio Santos27 abril 2025